New rules for anticancer vaccines
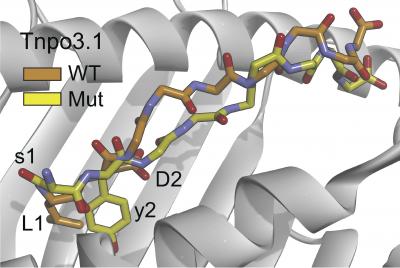
This simulation shows structural differences between mutant (yellow) and normal (orange) immune targets called neoepitopes. Researchers reveal how evaluating these distinctions can help pinpoint neoepitopes that elicit anticancer immune responses. Credit: Duan et al., 2014
As cancer cells divide, they accumulate random mistakes (mutations). This process creates new versions of proteins, some of which are recognized as foreign invaders by immune cells called T cells, prompting the cells to attack and eliminate the cancer cells.
With our current ability to identify all of the mutations in a patient's cancer and to understand which protein sequences can be recognized by T cells, scientists can now predict which mutations will result in new T cell targets (called “neoepitopes”). Some of these neoepitopes can then be used as vaccines to elicit a protective T cell response that destroys the cancer.
But here's the catch. These prediction tools generate hundreds of possible neoepitopes, of which only a handful can actually elicit T cells capable of attacking the tumor. And so far, there has been no reliable common denominator to help pinpoint this useful handful.
Previous attempts to predict cancer neoepitopes have relied on how strongly the mutated protein is recognized by the immune system. But scientists at the University of Connecticut now show that the strength of this interaction is a poor predictor. A better (albeit still imperfect) measure turns out to be how different the mutation looks to the T cell when compared to its normal counterpart—the more distinct, the better. These results have the potential to completely change current approaches to generating anticancer vaccines.
Duan, F., et al. 2014. J. Exp. Med. doi:10.1084/jem.20141308
About The Journal of Experimental Medicine
The Journal of Experimental Medicine (JEM) is published by The Rockefeller University Press. All editorial decisions on manuscripts submitted are made by active scientists in conjunction with our in-house scientific editors. JEM content is posted to PubMed Central, where it is available to the public for free six months after publication. Authors retain copyright of their published works and third parties may reuse the content for non-commercial purposes under a creative commons license. For more information, please visit http://www.jem.org .
Research reported in this press release was supported by Cancer Research Institute NY, Northeastern Utilities, Connecticut Institute for Clinical and Translational Science, SPARK, the National Science Foundation, the National Institutes of Health, Life Technologies, and the USDA National Institute of Food and Agriculture.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Health and Medicine
This subject area encompasses research and studies in the field of human medicine.
Among the wide-ranging list of topics covered here are anesthesiology, anatomy, surgery, human genetics, hygiene and environmental medicine, internal medicine, neurology, pharmacology, physiology, urology and dental medicine.
Newest articles

A universal framework for spatial biology
SpatialData is a freely accessible tool to unify and integrate data from different omics technologies accounting for spatial information, which can provide holistic insights into health and disease. Biological processes…

How complex biological processes arise
A $20 million grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) will support the establishment and operation of the National Synthesis Center for Emergence in the Molecular and Cellular Sciences (NCEMS) at…

Airborne single-photon lidar system achieves high-resolution 3D imaging
Compact, low-power system opens doors for photon-efficient drone and satellite-based environmental monitoring and mapping. Researchers have developed a compact and lightweight single-photon airborne lidar system that can acquire high-resolution 3D…





















