A newly discovered disease may lead to better treatment of cystic fibrosis
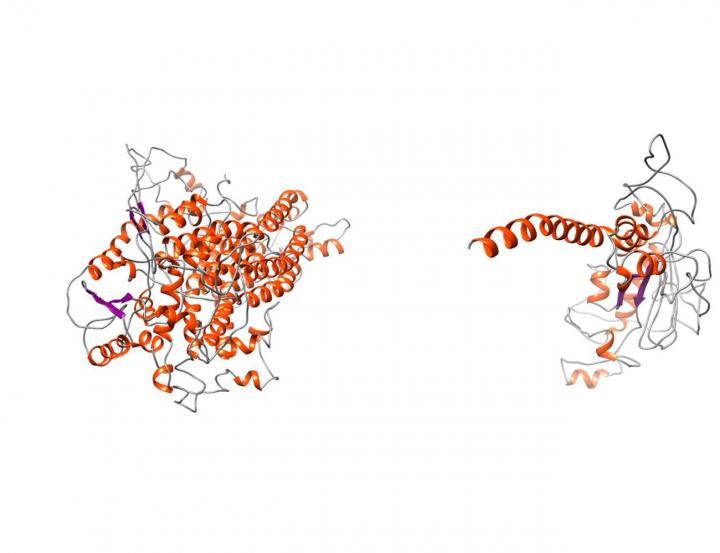
Comparison between the normal TMEM16A protein and the mutated variant showing the truncating effect that leads to the loss of vast portions of the protein. This leads to severe structural alterations. Credit: J. Park et al. 2020/ Journal of Medical Genetics Usage Restrictions: Please use this picture only in connection with the press release.
Cystic fibrosis is the most frequent severe inherited disorder worldwide. Every year, hundreds of families are confronted with this diagnosis – and to date, there is no cure for this disease that mainly affects the respiratory system.
Besides supportive treatments, a lung transplant is often the only option to save a patient's live. Researchers of the Universities of Münster and Regensburg have now discovered a novel disease that might lead to a better understanding of cystic fibrosis and new treatment options in the future. The results have been published in the scientific journal Journal of Medical Genetics.
The cause of cystic fibrosis are mutations in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductor regulator gene (CFTR). This gene contains the blueprint for a chloride channel on the surface of cells in the body. Normally, this channel mediates the accumulation of salt and fluids on the surface of the airways thereby leading to a continuous cleaning of the airways.
Defects in the CFTR channel prevent the transport of chloride ions and thus the humidification of the respiratory tract. As a result, the airways of affected individuals literally get plugged by a thickened, viscous mucus that leads to airway obstruction – patients are at the risk of suffocating.
At the University of Münster, the lab of Prof. Thorsten Marquardt has now discovered a new disease that is caused by defects in another chloride channel, TMEM16A. This channel is also present on the surface of airway cells.
In cooperation with the lab of Prof. Karl Kunzelmann of the University of Regensburg, the researchers evaluated the cellular effects of the disorder that is caused by a total loss of TMEM16A function. Surprisingly, they discovered that not only TMEM16A but also CFTR is not functional in these patients. Excitingly, this has the potential to improve the treatment of patients suffering from cystic fibrosis.
“We were astonished that children with TMEM16A deficiency don't have any respiratory symptoms at all. A loss of CFTR function due to lack of TMEM16A does not lead to clinincal symptoms of cystic fibrosis in these kids”, states Dr. Julien Park, first author and researcher at the Marquardt lab at the Department of General Pediatrics at the University Hospital Münster.
Similarly, the group of Prof. Karl Kunzelmann found in a mouse model that a double knock out of CFTR and TMEM16A does not develop lung disease.
Taken together, these results raise an intriguing question: Could the pharmacological inhibition of TMEM16A improve the respiratory symptoms of patients with cystic fibrosis?
A significant reduction of mucus production and secretion as a consequence of TMEM16A inhibition has previously been shown under laboratory conditions. The researchers want to study this approach further in the future: “As a next step, we are planning clinical trials to evaluate a treatment of cystic fibrosis with TMEM16A inhibitors”, states Karl Kunzelmann.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Health and Medicine
This subject area encompasses research and studies in the field of human medicine.
Among the wide-ranging list of topics covered here are anesthesiology, anatomy, surgery, human genetics, hygiene and environmental medicine, internal medicine, neurology, pharmacology, physiology, urology and dental medicine.
Newest articles

Sea slugs inspire highly stretchable biomedical sensor
USC Viterbi School of Engineering researcher Hangbo Zhao presents findings on highly stretchable and customizable microneedles for application in fields including neuroscience, tissue engineering, and wearable bioelectronics. The revolution in…

Twisting and binding matter waves with photons in a cavity
Precisely measuring the energy states of individual atoms has been a historical challenge for physicists due to atomic recoil. When an atom interacts with a photon, the atom “recoils” in…

Nanotubes, nanoparticles, and antibodies detect tiny amounts of fentanyl
New sensor is six orders of magnitude more sensitive than the next best thing. A research team at Pitt led by Alexander Star, a chemistry professor in the Kenneth P. Dietrich…





















