NASA analyzes Tropical Cyclone Cristina's water vapor concentration
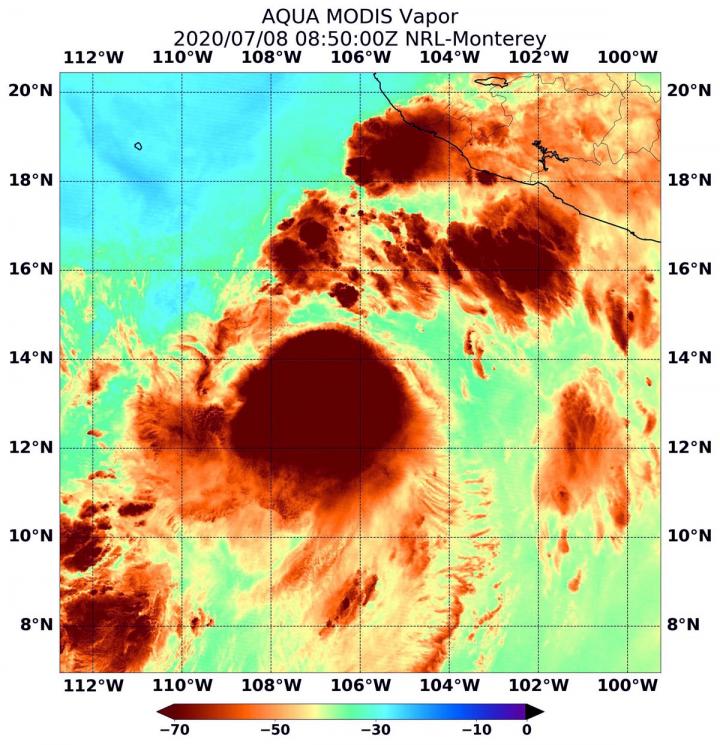
On July 8 at 4:50 a.m. EDT (0850 UTC) NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Cyclone Cristina, located in the Eastern Pacific Ocean. Aqua found highest concentrations of water vapor (brown) and coldest cloud top temperatures were around the center. Credits: NASA/NRL
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Cristina at 4:50 a.m. EDT (0850 UTC) and the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument gathered water vapor content and temperature information. The MODIS image showed highest concentrations of water vapor and coldest cloud top temperatures were around the center of circulation.
MODIS data also showed coldest cloud top temperatures were as cold as or colder than minus 70 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 56.6 degrees Celsius) in those storms. Storms with cloud top temperatures that cold have the capability to produce heavy rainfall.
Water vapor analysis of tropical cyclones tells forecasters how much potential a storm has to develop. Water vapor releases latent heat as it condenses into liquid. That liquid becomes clouds and thunderstorms that make up a tropical cyclone.
Temperature is important when trying to understand how strong storms can be. The higher the cloud tops, the colder and the stronger the storms.
The National Hurricane Center noted that satellite images show that the convective organization of Cristina is gradually improving, while bands of thunderstorms are developing across the northern portion of the circulation.
The center of Cristina's circulation was still under the northeastern side of the main area of convection due to moderate vertical wind shear, but that wind shear appears to be diminishing.
On July 8 at 11 a.m. EDT (1500 UTC), the center of Tropical Storm Cristina was located near latitude 14.6 degrees north and longitude 106.9 degrees west. That is about 350 miles (560 km) south-southwest of Manzanillo, Mexico.
Cristina is moving toward the northwest near 12 mph (19 kph). A turn to the west-northwest is expected by tonight, and that motion is expected to continue for the next few days. On the forecast track, the cyclone will remain well offshore the coast of Mexico. The estimated minimum central pressure is 998 millibars.
Maximum sustained winds are near 60 mph (95 kph) with higher gusts. Gradual strengthening is expected over the next couple of days, and Cristina is forecast to become a hurricane on Thursday.
National Hurricane Center forecaster Andrew Latto noted, “The decreasing shear over Cristina combined with warm sea surface temperatures and a moist air mass should allow the cyclone to intensify over the next couple of days.”
NASA's Aqua satellite is one in a fleet of NASA satellites that provide data for hurricane research.
Tropical cyclones/hurricanes are the most powerful weather events on Earth. NASA's expertise in space and scientific exploration contributes to essential services provided to the American people by other federal agencies, such as hurricane weather forecasting.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Artificial blood vessels could improve heart bypass outcomes
Artificial blood vessels could improve heart bypass outcomes. 3D-printed blood vessels, which closely mimic the properties of human veins, could transform the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Strong, flexible, gel-like tubes…

NASA’s Fermi finds new feature in brightest gamma-ray burst yet seen
In October 2022, astronomers were stunned by what was quickly dubbed the BOAT — the brightest-of-all-time gamma-ray burst (GRB). Now an international science team reports that data from NASA’s Fermi…

Folded peptides are more electrically conductive than unfolded peptides
Researchers combined single-molecule experiments, molecular dynamics simulations and quantum mechanics to validate the findings published in PNAS. What puts the electronic pep in peptides? A folded structure, according to a…





















