Elucidating Environmental History with 100 Million Laser Beams
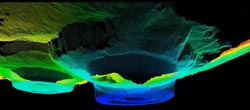
Digital 3D model of two dolines on Crete explored via high-precision laser scanning and subsurface measurement procedures. Vegetation such as olive trees and the surface of the soil were virtually removed for the models to provide insights into subsurface structure. Figure: Department of Geoinformatics<br>
By combining high-resolution surface data obtained from laser scanning with subsurface geodata, scientists from Heidelberg University have succeeded for the first time in providing a full picture of so-called karst depressions on the island of Crete, including a three-dimensional view into the subsurface structure of these funnel-shaped hollows.
This new 3D representation method has been developed under the leadership of junior professor Dr. Bernhard Höfle at Heidelberg University’s Institute of Geography. It is ideal for in-depth analyses at the interface between geosciences and ancient studies. The sediment infills of karst depressions provide terrestrial archives of great value for the reconstruction of environmental scenarios from the past.
For thousands of years, karst landforms and particularly karst depressions like dolines, for example, have been important sites of human husbandry. There is evidence from as far back as the 2nd century BC that such depressions were used for agriculture and livestock breeding, including in the mountainous regions of Crete. Due to their funnel-shaped form, dolines serve as “material traps” in which loose sediments, archaeological finds or volcanic ashes can accumulate. “These infills can supply important information on former climatic conditions, vegetation structure and also on human impact through land use”, says Dr. Christoph Siart, a fellow researcher of Prof. Höfle’s.
So far, say the Heidelberg geographers, karst depressions have usually only been examined in connection with drilling of sediment cores. These provide insights into the subsurface structure, albeit of a discrete nature, and have been drawn upon in conjunction with geomorphological surface finds to propose explanations for the genesis and function of dolines. With the aid of the new 3D data-modelling method developed in Heidelberg, the scientists have now succeeded in combining the two-dimensional subsurface data with high-resolution 3D surface data. To accomplish this, surface topography data were acquired with the aid of terrestrial laser scanning. Two-dimensional views of various cross-sections of the subsurface of the sediment-filled dolines were achieved with a combination of various geophysical measuring procedures.
The fusion of these data now makes it feasible to undertake soundly substantiated geomorphometric analyses. “For example, we can determine the volume or undertake a digital measurement of the depressions in a virtual three-dimensional model”, says Prof. Höfle. “That means we have created the basis for first-ever statements on the genesis, the sediment infill process and the age of the dolines. This is of immense significance for the reconstruction of the environmental history because it supplies a holistic view of geomorphological forms via a combination of surface and subsurface data and thus helps to understand the local processes that ultimately led to the formation of the landscape as we know it today.”
Data collection and methodological development took place in the framework of the projects “Reconstruction of Holocene Environmental Change on Crete” and “Geoinformatics and 3D Geoinformation Technology” conducted in the physical geography and geoinformatics research groups of Heidelberg University’s Institute of Geography. For more information, go to http://giscience.uni-hd.de.
Original publication
C. Siart, M. Forbriger, E. Nowaczinski, S. Hecht & B. Höfle: Fusion of multi-resolution surface (terrestrial laser scanning) and subsurface geodata (ERT, SRT) for karst landform investigation and geomorphometric quantification; Earth Surface Processes and Landforms (2013), doi: 10.1002/esp.3394
Contact
Junior professor Dr. Bernhard Höfle
Institute of Geography and
Heidelberg Center for the Environment (HCE)
Phone: +49 6221 54-5594
hoefle@uni-heidelberg.de
Communications and Marketing
Press Office, phone: +49 6221 54-2311
presse@rektorat.uni-heidelberg.de
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles
Faster, more energy-efficient way to manufacture an industrially important chemical
Zirconium combined with silicon nitride enhances the conversion of propane — present in natural gas — needed to create in-demand plastic, polypropylene. Polypropylene is a common type of plastic found…

Energy planning in Ghana as a role model for the world
Improving the resilience of energy systems in the Global South. What criteria should we use to better plan for resilient energy systems? How do socio-economic, technical and climate change related…

Artificial blood vessels could improve heart bypass outcomes
Artificial blood vessels could improve heart bypass outcomes. 3D-printed blood vessels, which closely mimic the properties of human veins, could transform the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Strong, flexible, gel-like tubes…





















