Discovery of faults on Pacific Ocean floor
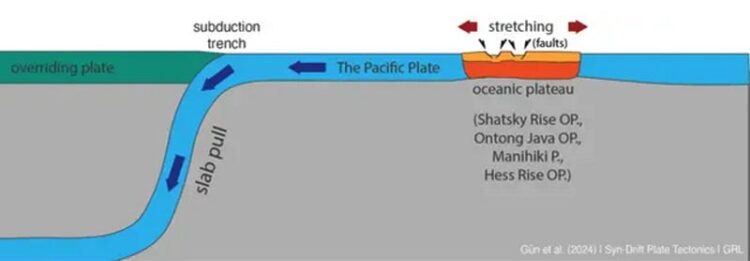
A cross-section showing how the sinking Pacific slab is stretching and pulling apart weak oceanic plateaux embedded in the Pacific Plate.
Credit: Erkan Gün & Russell Pysklywec/University of Toronto
Findings show Pacific Plate is being torn apart at undersea plateaus spanning the ocean by the weight of the oceanic plate subducting at the Western Pacific Ring of Fire.
New research led by a team of University of Toronto (U of T) geoscientists is refining the century-old model of plate tectonics that holds the plates covering the ocean floors are rigid as they move across Earth’s mantle.
Instead, the researchers found the Pacific Plate is scored by large undersea faults pulling it apart. The newly discovered faults, some thousands of metres deep and hundreds of kilometres long, are the result of enormous forces within the plate tugging it westward.
The map highlights in yellow the zones of the Pacific Plate that are being pulled apart by the sinking tectonic plate along the Pacific Ring of Fire. Credit: Erkan Gün & Russell Pysklywec/University of Toronto
The researchers describe their findings in a paper published in the journal Geophysical Research Letters. The authors include Erkan Gün, a postdoctoral fellow, and Professor Russell Pysklywec in the Department of Earth Sciences in the Faculty of Arts & Science at U of T, Phil Heron, an assistant professor in the Department of Physical & Environmental Sciences at University of Toronto Scarborough, as well as researchers from the Eurasia Institute of Earth Sciences, Istanbul Technical University.
“We knew that geological deformations like faults happen on the continental plate interiors far from plate boundaries,” says Gün. “But we didn’t know the same thing was happening to ocean plates.”
Says Pysklywec, “What we’re doing is refining plate tectonics — the theory that describes how our planet works — and showing those plates really aren’t as pristine as we previously thought.”
For millions of years, the Pacific Plate — which constitutes most of the floor of the ocean — has drifted westward to plunge down into Earth’s mantle along undersea trenches or subduction zones that run from Japan to New Zealand and Australia. As the western edge of the plate is pulled down into the mantle, it drags the rest of the plate with it like a tablecloth being pulled from a table.
The newly discovered plate damage at the faults occurs within extensive, sub-oceanic plateaus formed millions of years ago when molten rock from the Earth’s mantle extruded onto the ocean floor; the faults tend to run parallel to the closest trench.
“It was thought that because the sub-oceanic plateaus are thicker, they should be stronger,” says Gün. “But our models and seismic data show it’s actually the opposite: the plateaus are weaker.”
If the Pacific Plate is like a tablecloth being pulled across a tabletop, the plateaus are patches of weaker cloth more prone to tearing.
The researchers studied four plateaus in the western Pacific Ocean — the Ontong Java, Shatsky, Hess and Manihiki — in a vast area roughly bounded by Hawaii, Japan, New Zealand and Australia. They made their discovery using supercomputer models and existing data, some collected in studies done in the 1970s and 1980s.
“There is evidence that volcanism occurred at these sites in the past as a result of this type of plate damage — perhaps episodically or continuously — but it isn’t clear if that’s happening now,” says Gün. “Still, we can’t be certain because the plateaus are thousands of metres below the ocean surface and sending research vessels to collect data is a major effort. So, in fact, we’re hopeful our paper brings some attention to the plateaus and more data will be collected.”
The theory of plate tectonics has been refined over many decades by numerous earth scientists — including U of T’s John Tuzo Wilson who made significant contributions to it during his career.
“But the theory is not carved in stone and we’re still finding new things,” says Pysklywec. “Now we know this fault damage is tearing apart the centre of an ocean plate —and this could be linked to seismic activity and volcanism.
“A new finding like this overturns what we’ve understood and taught about the active Earth”, he says. “And it shows that there are still radical mysteries about even the grand operation of our evolving planet.”
MEDIA CONTACTS:
Erkan Gün
Department of Earth Sciences
University of Toronto
erkan.gun@utoronto.ca
Russell Pysklywec
Department of Earth Sciences
University of Toronto
r.pysklywec@utoronto.ca
Sean Bettam
Communications & Public Affairs, Faculty of Arts & Science
University of Toronto
s.bettam@utoronto.ca
Journal: Geophysical Research Letters
DOI: 10.1029/2023GL105452
Method of Research: Computational simulation/modeling
Subject of Research: Not applicable
Article Title: Syn-Drift Plate Tectonics
Article Publication Date: 21-Jan-2024
All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles
Faster, more energy-efficient way to manufacture an industrially important chemical
Zirconium combined with silicon nitride enhances the conversion of propane — present in natural gas — needed to create in-demand plastic, polypropylene. Polypropylene is a common type of plastic found…

Energy planning in Ghana as a role model for the world
Improving the resilience of energy systems in the Global South. What criteria should we use to better plan for resilient energy systems? How do socio-economic, technical and climate change related…

Artificial blood vessels could improve heart bypass outcomes
Artificial blood vessels could improve heart bypass outcomes. 3D-printed blood vessels, which closely mimic the properties of human veins, could transform the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Strong, flexible, gel-like tubes…





















