Erasable ink for 3-D printing
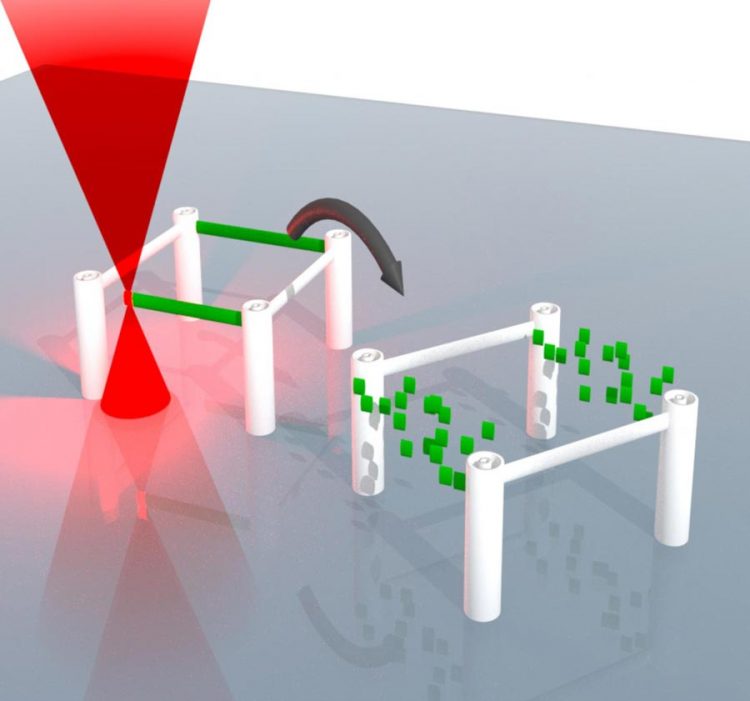
3-dimensional microstructures can be written using a laser, erased, and rewritten. Photo: KIT
3D printing by direct laser writing produces micrometer-sized structures with precisely defined properties. Researchers of Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) have now developed a method to erase the ink used for 3D printing.
In this way, the small structures of up to 100 nm in size can be erased and rewritten repeatedly. One nanometer corresponds to one millionth of a millimeter. This development opens up many new applications of 3D fabrication in biology or materials sciences, for instance.
Direct laser writing means that a computer-controlled, focused laser beam generates the structure in a photoresist similar to a pen. “Developing an ink that can be erased again was one of the big challenges in direct laser writing,” Professor Christopher Barner-Kowollik of KIT's Institute for Chemical Technology and Polymer Chemistry says.
The scientists have now met with success: They have developed an ink with reversible bonding, the building blocks of which can be separated from each other. The printed structure is simply erased by immersing it into a chemical solvent. At the point of erasure, a new structure can be written. In this way, the structure can be modified repeatedly.
The process was developed in close cooperation with the group of Professor Martin Wegener at the Institute of Applied Physics and the Institute of Nanotechnology of KIT. The physicists developed highly specialized 3D printers that produce scaffolds of up to 100 nm in size by direct laser writing.
“The ink with defined breaking points can be used for a variety of applications,” doctoral student and first author Markus Zieger says. Structures written with erasable ink can be integrated into structures made of non-erasable ink: Support constructions can be produced by 3D printing, which are similar to those used when building bridges and removed later on. It is also possible to further develop 3D designer petri dishes for use in biology. Recently, such structures were designed by KIT to grow cell cultures in three dimensions on the laboratory scale.
“During cell growth, parts of the 3D microscaffold could be removed again to study how the cells react to the changed environment,” Martin Wegener explains. According to the scientists, it is also feasible to produce reversible wire bonds from erasable conducting structures in the future. A permanent ink can be mixed with a non-permanent ink to influence the properties of the printed material and make it more or less porous, for instance.
The new process is presented in the renowned journal Angewandte Chemie under the heading “Cleaving Direct Laser Written Microstructures on Demand.” The reviewers rated this publication a “very important paper.” 3D printing already is indispensable in many fabrication areas. Its importance is increasing. “According to estimations, some 10 percent of all goods will be produced by 3D printing in 2030,” Barner-Kowollik and Wegener say.
###
Markus M. Zieger, Patrick Mueller, Alexander S. Quick, Martin Wegener, Christopher Barner-Kowollik: Cleaving Direct Laser Written Microstructures on Demand. Angewandte Chemie 2017, 129, 1-6; DOI: 10.1002/anie.201701593
Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) pools its three core tasks of research, higher education, and innovation in a mission. With about 9,300 employees and 25,000 students, KIT is one of the big institutions of research and higher education in natural sciences and engineering in Europe.
KIT – The Research University in the Helmholtz Association
afr, 24.04.2017
For further information, please contact:
Kosta Schinarakis
Themenscout
Tel.: +49 721 608-41956
Fax: +49 721 608-43568
E-Mail:schinarakis@kit.edu
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

A universal framework for spatial biology
SpatialData is a freely accessible tool to unify and integrate data from different omics technologies accounting for spatial information, which can provide holistic insights into health and disease. Biological processes…

How complex biological processes arise
A $20 million grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) will support the establishment and operation of the National Synthesis Center for Emergence in the Molecular and Cellular Sciences (NCEMS) at…

Airborne single-photon lidar system achieves high-resolution 3D imaging
Compact, low-power system opens doors for photon-efficient drone and satellite-based environmental monitoring and mapping. Researchers have developed a compact and lightweight single-photon airborne lidar system that can acquire high-resolution 3D…





















