Correcting presbyopia with the laser
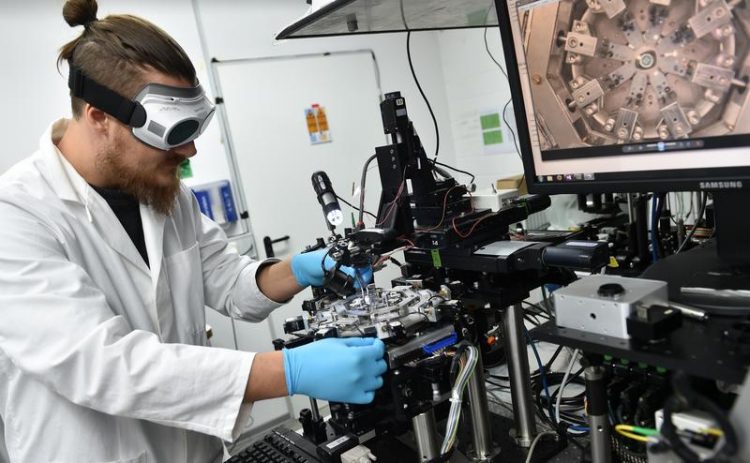

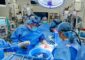
In order to better predict eye surgeries in the future, scientists at the LZH have developed both a mechanics as well as an optics model of the eye. Photo: LZH
For the RayFEye project, the scientists of the LZH have developed both a mechanics and an optics model.
The mechanical model was used on test eyes (a by-product of the animal) to examine how laser incisions in the lens and the cornea influence their refraction behavior.
Based on these data, the researchers then developed a biomechanical model that can also be analyzed for optical imaging performance.
The model is supposed to predict the optimal placement and the expected vision of the patient before surgery.
The long-term goal is to develop gentle surgical methods and to replace clinical studies through virtual studies.
About RayFEye
In addition to the LZH, the Optimo Medical AG (formerly Integrated Scientific Services AG), which is developing the OptimEyesTM software, and the ROWIAK GmbH, the manufacturer of the laser system, are involved in the project.
The joint project “Ray tracing in ophthalmic finite element models for predicting visual acuity enhancement” (RayFEye) was funded within the framework of the Eurostars program by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) and by the Swiss State Secretariat for Education, Research and Innovation (SERI) under the grant number 01QE1545B.
Laser Zentrum Hannover e.V.
Dipl.-Biol. Lena Bennefeld
Communication Department
Hollerithallee 8
D-30419 Hannover
Germany
Tel.: +49 511 2788-238
Fax: +49 511 2788-100
E-Mail: presse@lzh.de
Internet: www.lzh.de
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Medical Engineering
The development of medical equipment, products and technical procedures is characterized by high research and development costs in a variety of fields related to the study of human medicine.
innovations-report provides informative and stimulating reports and articles on topics ranging from imaging processes, cell and tissue techniques, optical techniques, implants, orthopedic aids, clinical and medical office equipment, dialysis systems and x-ray/radiation monitoring devices to endoscopy, ultrasound, surgical techniques, and dental materials.
Newest articles

A universal framework for spatial biology
SpatialData is a freely accessible tool to unify and integrate data from different omics technologies accounting for spatial information, which can provide holistic insights into health and disease. Biological processes…

How complex biological processes arise
A $20 million grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) will support the establishment and operation of the National Synthesis Center for Emergence in the Molecular and Cellular Sciences (NCEMS) at…

Airborne single-photon lidar system achieves high-resolution 3D imaging
Compact, low-power system opens doors for photon-efficient drone and satellite-based environmental monitoring and mapping. Researchers have developed a compact and lightweight single-photon airborne lidar system that can acquire high-resolution 3D…