Moving molecule writes letters
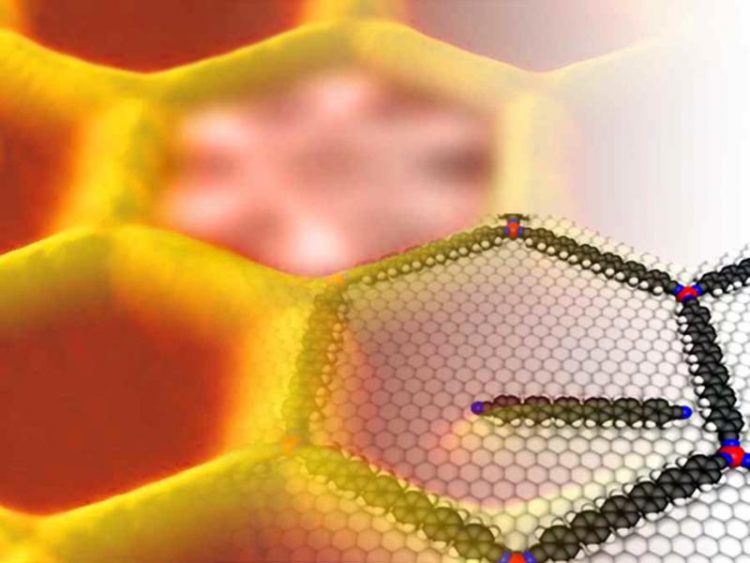
The nanopore restricts the the freedom of movement of the adsorbed single molecule thus enabling scientists at Technische Universitat Munchen and University Lingkoping to model the equilibrium thermodynamics of single molecules. Credit: Carlos-Andres Palma / TUM
On the search for high performance materials for applications such as gas storage, thermal insulators or dynamic nanosystems it is essential to understand the thermal behavior of matter down to the molecular level. Classical thermodynamics average over time and over a large number of molecules. Within a three dimensional space single molecules can adopt an almost infinite number of states, making the assessment of individual species nearly impossible.
Now researchers from Technische Universität München (TUM) and Linköping University (LIU) have developed a methodology, which allows to explore equilibrium thermodynamics of single molecules with atomic resolution at appreciable temperatures. The breakthrough study is based on two pillars: a technology which allows to cage molecules within two-dimensional nanopores and extensive computational modelling.
Trapped in two dimensions
At the Chair of Molecular Nanoscience and Chemical Physics of Interfaces at TU München, led by Prof. Dr. Johannes V. Barth, PD Dr. Florian Klappenberger developed the method to produce high-quality metal-organic networks on a silver surface. The network forms nanopores which restrict the freedom of movement of adsorbed single molecules in two-dimensions. Using scanning tunneling microscopy the researchers were able to track their motions at different temperatures with sub-nanometer resolution.
Parallel to the experiments, the researchers worked with sophisticated computer models to describe the temperature dependence of the dynamics of these single trapped molecules. “We have applied state-of-the-art supercomputer calculations to understand the interactions and energy landscape determining the motion of the molecules”, says Jonas Björk of Linköping University.
Comparing experimental and modeled data the scientists unraveled that under certain conditions the integral theory approaches a simple projection of the molecular positions in space. This approach is central to statistical mechanics, but has never before been challenged to reproduce an experiment, due to the practically infinite molecular positions and energies one needed to consider without the nanoscale confinement.
Analogy to biology
“It was extremely exciting to employ two-dimensional networks as a confinement strategy to reduce the available conformational space of a single molecule, like a chaperone does with a protein”, says Dr. Carlos-Andres Palma, the lead author of the study. “In analogy to biology, such form of confinement technology has the potential to establish sensors, nanomachines and possibly logics controlled by and made of molecular distributions.”
Applying their knowledge of characteristic equilibrium configurations, the researchers carefully modulated the nanopore, thus making a single molecule write letters of the alphabet such as L, I and U, just by fine-tuning the temperature.
The research was funded by the European Research Council (ERC Advanced Grant MolArt) and the Swedish Research Council. The Swedish National Supercomputing Center provided supercomputing ressources. The research group of Professor Barth is member of the Catalysis Research Center (CRC) of the TUM.
Publication:
Visualization and thermodynamic encoding of single-molecule partition function projections
Carlos-Andres Palma, Jonas Björk, Florian Klappenberger, Emmanuel Arras, Dirk Kühne, Sven Stafström, Johannes V. Barth
Nature Communications, Feb 23, 2015 – DOI: 10.1038/ncomms7210
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Sea slugs inspire highly stretchable biomedical sensor
USC Viterbi School of Engineering researcher Hangbo Zhao presents findings on highly stretchable and customizable microneedles for application in fields including neuroscience, tissue engineering, and wearable bioelectronics. The revolution in…

Twisting and binding matter waves with photons in a cavity
Precisely measuring the energy states of individual atoms has been a historical challenge for physicists due to atomic recoil. When an atom interacts with a photon, the atom “recoils” in…

Nanotubes, nanoparticles, and antibodies detect tiny amounts of fentanyl
New sensor is six orders of magnitude more sensitive than the next best thing. A research team at Pitt led by Alexander Star, a chemistry professor in the Kenneth P. Dietrich…





















