Protein translation in sperm

A new paper in the February 15th issue of Genes & Development lends novel insight into the cellular changes that occur in sperm while they reside in the female reproductive tract – providing a new understanding of the molecular genetics of successful fertilization.
It had been believed for decades that spermatozoa are translationally silent. However, Dr. Yael Gur and Haim Breitbart (Bar-Ilan University, Israel) now show that, in fact, protein translation does take place in mammalian sperm prior to fertilization.
Their paper has been released online ahead of print at www.genesdev.org.
After ejaculation, sperm reside in the female reproductive tract for several hours. During this time, a number of biochemical changes take place within sperm, collectively known as “capacitation,” that render the sperm competent to penetrate and fertilize the female oocyte.
In their new report, Drs. Gur and Breitbart demonstrate that human, rat, bovine and mouse sperm all incorporate labeled amino acids into polypeptides during the capacitation phase. They identify that mitochondrial translation machinery (as opposed to cytoplasmic) directs translation of nuclear-encoded genes in sperm, and that its inhibition leads to a marked decrease in sperm motility, actin polymerization, the acrosome reaction and in vitro fertilization rates.
Thus, protein translation in sperm is essential for sperm functions that directly contribute to fertilization. Dr. Breitbart is confident that “The new findings would give us better understanding for treatment of male infertility and developing new male or female contraceptives.”
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

How evolution has optimised the magnetic sensor in birds
The magnetic sense of migratory birds is probably based on the protein cryptochrome 4, and a genetic study has now provided further support for this theory. A team of researchers…
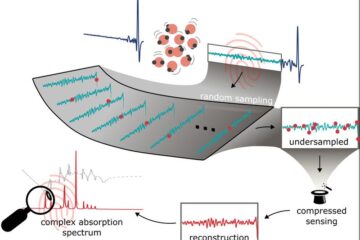
Molecular Fingerprint Beyond the Nyquist Frequency
Ultrafast laser spectroscopy allows the ascertainment of dynamics over extremely short time scales, making it a very useful tool in many scientific and industrial applications. A major disadvantage is the…

High-energy-density aqueous battery based on halogen multi-electron transfer
Traditional non-aqueous lithium-ion batteries have a high energy density, but their safety is compromised due to the flammable organic electrolytes they utilize. Aqueous batteries use water as the solvent for…





















