A marker for new blood vessel formation in tumors
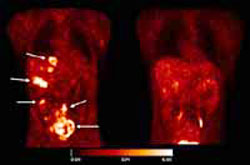
ávâ3 integrin expression in tumors. (Photo: Roland Haubner, et al.)
In a paper in this month’s freely-available online global health journal PLoS Medicine, Roland Haubner and colleagues describe how a compound they have developed can be used together with highly sensitive positron emission tomography (PET) scanning to measure the amount of new blood vessel growth in some tumors.
New blood vessel growth – angiogenesis – is important for the growth of tumors; several drugs target angiogenesis specifically. The compound previously developed by Haubner and colleagues is a fluorine-labeled glycopeptide, ([18F]Galacto-RGD), which binds tightly to a receptor – ávâ3 integrin -expressed in some tumors, especially in the blood vessels. As well as a role in angiogenesis, integrins are important in holding tumor cells together and connecting them with the extracellular matrix; what happens when these interactions break down is one of the keys to determining how tumors metastasize.
Haubner and colleagues’ work, in a mouse with human melanoma and in a small study of patients with tumors including melanoma, suggests that the marker is truly reflecting the in vivo level of the integrin. Hence the marker could be used to identify tumors that express this marker, assess the degree of new vessel formation in tumors, and help in the planning and monitoring of anti-angiogenic therapies which target this integrin.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.plos.orgAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

A universal framework for spatial biology
SpatialData is a freely accessible tool to unify and integrate data from different omics technologies accounting for spatial information, which can provide holistic insights into health and disease. Biological processes…

How complex biological processes arise
A $20 million grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) will support the establishment and operation of the National Synthesis Center for Emergence in the Molecular and Cellular Sciences (NCEMS) at…

Airborne single-photon lidar system achieves high-resolution 3D imaging
Compact, low-power system opens doors for photon-efficient drone and satellite-based environmental monitoring and mapping. Researchers have developed a compact and lightweight single-photon airborne lidar system that can acquire high-resolution 3D…





















