At the Right Place at the Right Time – New Insights into Muscle Stem Cells
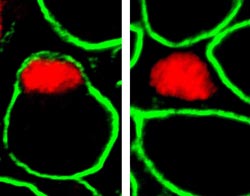
In healthy mice a stem cell (red) resides in a special niche between the muscle cell and the basal lamina (green) (left) which surrounds it. If the Notch signaling pathway is mutated, the stem cell locates outside of the muscle fiber (right) and hardly contributes to muscle growth.<br><br>(Photo: Dominique Bröhl/ Copyright: MDC)<br>
The stem cells must reside in special niches of the muscle for efficient growth and repair. The developmental biologists Dr. Dominique Bröhl and Prof. Carmen Birchmeier of the Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine (MDC) Berlin-Buch have elucidated how these stem cells colonize these niches.
At the same time, they show that the stem cells weaken when, due to a mutation, they locate outside of the muscle fibers instead of in their stem cell niches (Developmental Cell, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2012.07.014)*.
Muscle stem cells, also called satellite cells, colonize a niche that is located between the plasma membrane of the muscle cell and the surrounding basal lamina. Already in newborns these niches contain satellite cells from which both muscle cells and new stem cells can be generated.
Weakened stem cells
In the present study Dr. Bröhl and Professor Birchmeier showed that mouse muscle progenitor cells lacking components of the Notch signaling pathway cannot colonize their niche. Instead the muscle progenitor cells locate in tissue between the muscle fibers. The developmental biologists view this as the cause for the weakening of the muscles. The stem cells that are “in the wrong place” are no longer as potent as they originally were and hardly contribute to muscle growth.
In addition, the Notch signaling pathway has a second function in muscle development. It prevents the differentiation of stem cells into muscle cells through suppression of the muscle developmental factor MyoD and thus ensures that there will always be a pool of stem cells for muscle repair and regeneration. In the future this work could gain in importance for research on muscle regeneration and muscle weakness.
*Colonization of the Satellite Cell Niche by Skeletal Muscle Progenitor Cells Depends on Notch Signals
Dominique Bröhl1, Elena Vasyutina1,#, Maciej T. Czajkowski1, Joscha Griger1, Claudia Rassek1, Hans-Peter Rahn2, Bettina Purfürst3, Hagen Wende1 and Carmen Birchmeier1*
1Developmental Biology/Signal Transduction Group, 2Preparative Flow Cytometry and 3Electron Microscopy Core Facility
Max-Delbrück-Center for Molecular Medicine, Robert-Rössle-Str. 10, 13125 Berlin, Germany
Contact:
Barbara Bachtler
Press Department
Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine (MDC) Berlin-Buch
in the Helmholtz Association
Robert-Rössle-Straße 10; 13125 Berlin, Germany
Phone: +49 (0) 30 94 06 – 38 96; Fax: +49 (0) 30 94 06 – 38 33
e-mail: presse@mdc-berlin.de
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.mdc-berlin.de/All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

A universal framework for spatial biology
SpatialData is a freely accessible tool to unify and integrate data from different omics technologies accounting for spatial information, which can provide holistic insights into health and disease. Biological processes…

How complex biological processes arise
A $20 million grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) will support the establishment and operation of the National Synthesis Center for Emergence in the Molecular and Cellular Sciences (NCEMS) at…

Airborne single-photon lidar system achieves high-resolution 3D imaging
Compact, low-power system opens doors for photon-efficient drone and satellite-based environmental monitoring and mapping. Researchers have developed a compact and lightweight single-photon airborne lidar system that can acquire high-resolution 3D…





















