Good vibrations for the future of computing
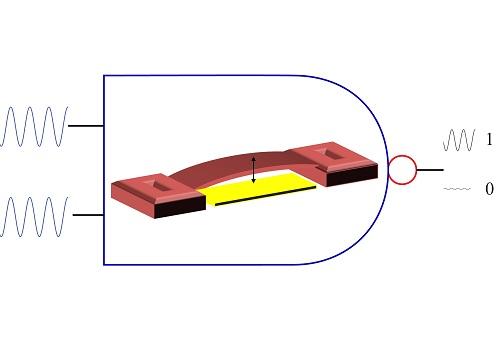
The cascadable, vibration-driven microelectromechanical logic gate takes electrical signals as inputs and produces a logic output (1 or 0) based on the resonance of the microbeam. Credit: © 2016 KAUST
The microcomputer processors found inside every computer, mobile phone and microwave comprise mind-bogglingly complex networks of millions or billions of microscopic transistors — electrical switches that turn on when a current flows across their terminals.
These transistors are networked together to construct logic gates that perform operations, such as AND (when two inputs are on) and OR (when either input is on). In turn, these logic gates are connected to much larger networks to allow increasingly complex operations.
With each transistor consuming electrical current and generating heat even when not being actively switched, and with transistors approaching their physical limits of miniaturization and efficiency, the search is on for alternative technology that will eventually replace the electrical transistor and take computing into the future.
Saad Ilyas and Nizar Jaber, doctoral researchers in the laboratory of Mohammad Younis, have now demonstrated a scalable, efficient alternative technology, not based on electrical current, but on mechanical vibrations excited by multifrequency electrical inputs.
“Electromechanical systems offer a major advantage over existing technology in that they are leakage free: that is, unlike electrical transistors, they only consume power when switched,” explains Ilyas. “They also require fewer gates per computing function, resulting in lower complexity, and they can be fabricated with higher integration densities — it is even predicted that these systems could be scaled down to the molecular level.”
Microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) have been investigated in the past for logic operations, but it has been a challenge to devise a mode of operation that allows the MEMS logic gates to be cascaded to form arbitrary computational functions. Jaber and Younis have come up with a novel technique to perform logic operations using MEMS based on frequency mixing, which holds great potential for cascading.
“We use an electrical signal as an input, which causes a clamped polymer microbeam to vibrate at a certain resonance frequency,” says Jaber. “This in turn generates motional current as an electrical signal with the same frequency, which could then be cascaded into the input of another MEMS logic gate.”
The team demonstrated various logic operations at a single operating frequency, which is an important step towards cascading as the next milestone in MEMS resonator-based computing. Their logic gates are also compatible with existing fabrication techniques.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Information Technology
Here you can find a summary of innovations in the fields of information and data processing and up-to-date developments on IT equipment and hardware.
This area covers topics such as IT services, IT architectures, IT management and telecommunications.
Newest articles

A universal framework for spatial biology
SpatialData is a freely accessible tool to unify and integrate data from different omics technologies accounting for spatial information, which can provide holistic insights into health and disease. Biological processes…

How complex biological processes arise
A $20 million grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) will support the establishment and operation of the National Synthesis Center for Emergence in the Molecular and Cellular Sciences (NCEMS) at…

Airborne single-photon lidar system achieves high-resolution 3D imaging
Compact, low-power system opens doors for photon-efficient drone and satellite-based environmental monitoring and mapping. Researchers have developed a compact and lightweight single-photon airborne lidar system that can acquire high-resolution 3D…