'Twist and shine': Development of a new photoluminescent sensor material
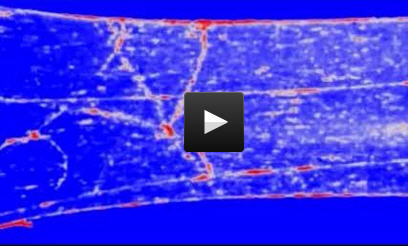
The polymer material is stretched with an increasing force resulting in a corresponding brighter emission of light from the mechanophore (here under UV light and with false colors). The graph shows the intensity of the emitted light following punctual increases in the stretching force applied to the polymer. Credit: OIST
Stress sensors are important tools when it comes to evaluating the robustness of a material facing strong mechanical forces. OIST researchers have just published in Advanced Materials an article reporting a new kind of sensor molecules that brightens up when the material they are incorporated into comes under heavy mechanical stress.
Such light-based sensing molecules, also called photoluminescent mechanophores, are not new, but currently available applications are single-use only. They would typically involve a strong force — compressing, twisting or stretching for example — breaking a specific chemical bond between two atoms or irreversibly pulling apart two molecular patterns in the sensing molecule, changing the wavelength – and thus the color – of the light emitted by the mechanophore.
Once these molecules have radically changed their structure in response to this force, it is extremely difficult to return to the initial situation. While these mechanophores are useful to understand the mechanical properties of an item or a material, they do not suit well for repeated exposure to mechanical stress.
To overcome this issue, Dr. Georgy Filonenko and Prof. Julia Khusnutdinova from the Coordination Chemistry and Catalysis Unit designed a photoluminescent mechanophore that retains its properties over time and under repeated incidences of mechanical stress.
The researchers incorporated the stress-sensing molecule into a common polymer material called polyurethane, widely used for everyday items from mattresses and cushions to inflatable boats, car interiors, woodworking glue and even spandex.
The scientists then stretched the resulting material with increasing force, triggering a correspondingly brighter glow under an ultraviolet light. The reaction happens within hundreds of milliseconds, resulting in a up to two-fold increase in luminescence intensity. When the mechanical traction stops, the polymer material and the mechanophore reverse to their initial position, decreasing the light readout. This is critical as it allows for repeated applications of mechanical force.
This new mechanophore is a photoluminescent compound from recently published work by Dr. Filonenko and Prof. Khusnutdinova. Despite its very simple structure the compound is extremely responsive to the physical environment which has a direct impact on the color visible with the naked eye under a UV light. These molecules were incorporated directly within the repeated patterns of the polymer material.
The high mobility of the mechanophore molecules in the polymer was found to be the key to the sensor performance. As mechanophores moved rapidly in the relaxed polymer sample, the brightness of emission was low due to these molecular motions preventing the mechanophore from emitting light. However, subjecting the material to mechanical force effectively slowed down the polymer chain motions, enabling the mechanophore to emit light more efficiently.
“Our material shows how a macroscopic force, as basic as stretching a flexible strand of material, can efficiently trigger microscopic changes all the way down to isolated molecules,” commented Dr. Filonenko.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

A universal framework for spatial biology
SpatialData is a freely accessible tool to unify and integrate data from different omics technologies accounting for spatial information, which can provide holistic insights into health and disease. Biological processes…

How complex biological processes arise
A $20 million grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) will support the establishment and operation of the National Synthesis Center for Emergence in the Molecular and Cellular Sciences (NCEMS) at…

Airborne single-photon lidar system achieves high-resolution 3D imaging
Compact, low-power system opens doors for photon-efficient drone and satellite-based environmental monitoring and mapping. Researchers have developed a compact and lightweight single-photon airborne lidar system that can acquire high-resolution 3D…





















