Creating a reference map to explore the electronic device mimicking brain activity
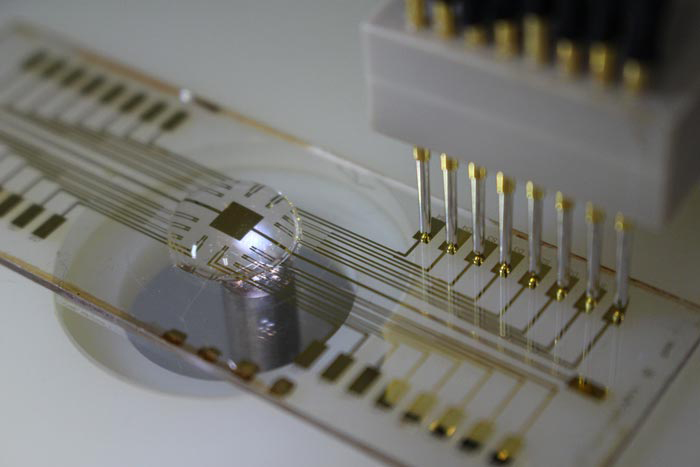
An image of an OECT device studied in this work
Credit: Shusuke Yamamoto
Maps are essential for exploring trackless wilderness or vast expanses of ocean. The same is true for scientific studies that try to open up new fields and develop brand-new devices. A journey without maps and signposts tends to end in vain.
In the world of “neuromorphic devices,” an electronic device that mimics neural cells such as our brain, researchers have long been forced to travel without maps. Such devices will lead to a fresh field of brain-inspired computers with substantial benefits such as low-energy consumption. But its operation mechanism has remained unclear, particularly in regards to controlling the response speed control.
A research group from Tohoku University and the University of Cambridge brought clarity in a recent study published in the journal Advanced Electronic Materials on January 13, 2022.
They looked into organic electrochemical transistors (OECT), which are often applied in neuromorphic devices and control the movement of the ion in the active layer. The analysis revealed that response timescale depends on the size of ion in the electrolyte.
Based on these experimental results, the group modeled the neuromorphic response of the devices. Comparisons of the data showed that movements of the ions in the OECT controlled the response. This indicates tuning the timescale for ion movement can be an effective way to regulate the neuromorphic behavior of OECTs.
“We obtained a map that provides rational design guidelines for neuromorphic devices through changing ion size and material composition in the active layer,” said Shunsuke Yamamoto, paper corresponding author and assistant professor at Tohoku University’s Graduate School of Engineering. “Further studies will pave the way for application to artificial neural networks and lead to better and more precise designs of the conducting polymer materials used in this field.”
Journal: Advanced Electronic Materials
DOI: 10.1002/aelm.202101186
Article Title: Correlation between Transient Response and Neuromorphic Behavior in Organic Electrochemical Transistors
Article Publication Date: 13-Jan-2022
Media Contact
Public Relations
Tohoku University
public_relations@grp.tohoku.ac.jp
All latest news from the category: Power and Electrical Engineering
This topic covers issues related to energy generation, conversion, transportation and consumption and how the industry is addressing the challenge of energy efficiency in general.
innovations-report provides in-depth and informative reports and articles on subjects ranging from wind energy, fuel cell technology, solar energy, geothermal energy, petroleum, gas, nuclear engineering, alternative energy and energy efficiency to fusion, hydrogen and superconductor technologies.
Newest articles

Microscopic basis of a new form of quantum magnetism
Not all magnets are the same. When we think of magnetism, we often think of magnets that stick to a refrigerator’s door. For these types of magnets, the electronic interactions…

An epigenome editing toolkit to dissect the mechanisms of gene regulation
A study from the Hackett group at EMBL Rome led to the development of a powerful epigenetic editing technology, which unlocks the ability to precisely program chromatin modifications. Understanding how…

NASA selects UF mission to better track the Earth’s water and ice
NASA has selected a team of University of Florida aerospace engineers to pursue a groundbreaking $12 million mission aimed at improving the way we track changes in Earth’s structures, such…





















