Cooperative operations between a solar observation satellite and a sounding-rocket telescope have measured the magnetic field strength in the photosphere and chromosphere above an active solar plage region. This is the first time that the magnetic field in the chromosphere has been charted all the way up to its top. This finding brings us closer to understanding how energy is transferred between layers of the Sun.
Despite being the brightest object in the sky, the Sun still holds many mysteries for astronomers. It is generally believed that magnetic fields play an important role in heating the solar corona, but the details of the process are still unclear. To solve this mystery it is important to understand the magnetic field in the chromosphere, which is sandwiched between the corona and the photosphere, the visible surface of the Sun.
An international team led by Ryohko Ishikawa, an assistant professor at the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan, and Javier Trujillo Bueno, a professor at the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, analyzed data collected by the CLASP2 sounding rocket experiment over twosix-and-a-half-minutes on April 11, 2019. They determined the longitudinal component of the magnetic field above an active region plage and its surroundings by analyzing the signature that the magnetic field imprinted on ultraviolet light from the chromosphere.
The unique high precision data from CLASP2 allowed the team to determine the magnetic field strengths in the lower, mid, and upper regions of the chromosphere. Simultaneously acquired data from the Japanese solar observation satellite Hinode provided information about the magnetic field in the plage itself in the photosphere.
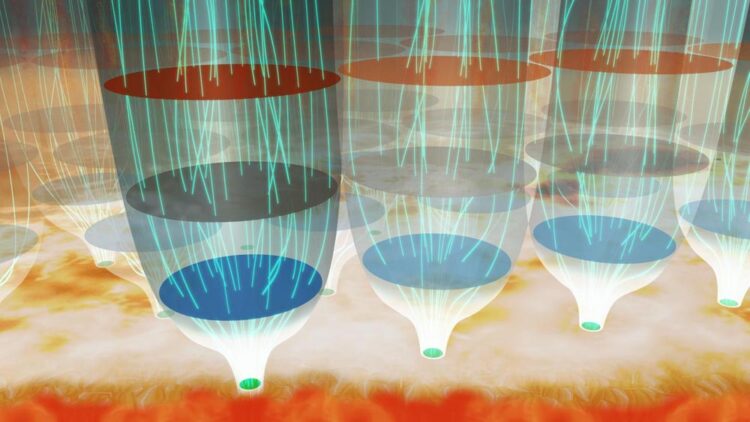
The team found that the plage magnetic field is highly structured in the photosphere but expands, rapidly merging and spreading horizontally, in the chromosphere. This new picture brings us closer to understanding how magnetic fields transfer energy to the corona from the lower layers of the Sun.
These results appeared as Ishikawa et al. “Mapping Solar Magnetic Fields from the Photosphere to the Base of the Corona,” in Science Advances on February 19 2021.