New Type of Friction Discovered in Ligand-Protein Systems
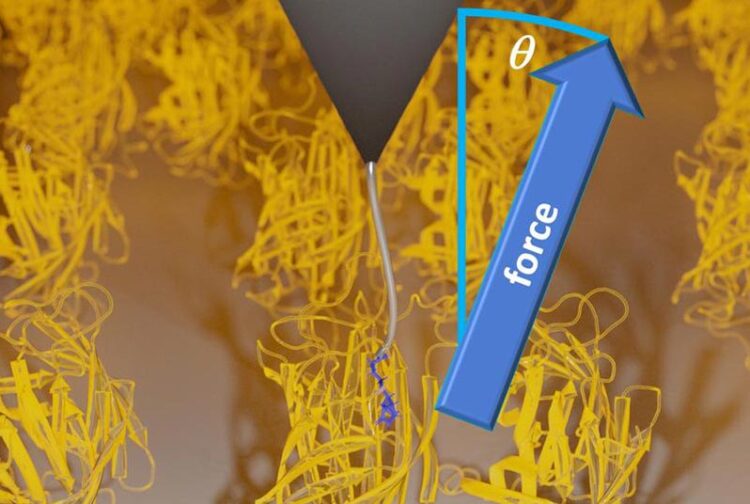
Pulling experiments on a biotin-streptavidin complex. Biotin (blue lines) is pulled out of a streptavidin protein (yellow) via a polymer linker (gray line), which is bound to a cantilever tip of an atomic force microscope (gray triangle).
Image source: Dr. Steffen Wolf / University of Freiburg
- A team from the University of Freiburg and the Max Planck Institute of Biophysics in Frankfurt-am-Main identify anisotropic friction
- In their investigation, the researchers applied new methods of single molecule force spectroscopy and high performance computing
- The results provide a key piece of the puzzle for understanding friction in technical applications and biological complexes
An interdisciplinary research team of the Institutes of Physical Chemistry and Physics of the University of Freiburg and the Max Planck Institute of Biophysics in Frankfurt-am-Main has discovered a new, direction-dependent friction in proteins called anisotropic friction. “Until now, nobody had observed that friction in biomolecules was dependent on direction,” says physicist Dr. Steffen Wolf of the University of Freiburg. The results have been published as cover story in the scientific journal “Nano Letters.”
Experiments on model complex of protein-ligands
Proteins constitute the microscopic machinery of cells. They perform work during their functional cycles. Accordingly, they follow the laws of thermodynamics, exhibit an energy conversion efficiency, and lose energy during their functional cycle due to dissipation. From a macroscopic perspective, the latter effect corresponds to apparent friction. On the microscopic scale of single proteins, a known source of friction is internal friction of proteins that results from the excitation of protein-internal vibrations. A further source is solvent friction, which arises from the acceleration of surrounding solvent molecules. These sources of friction lead to heating of both protein and solvent. Here, the researchers discovered the novel type of friction by carrying out single molecule experiments and simulations on a model complex of a protein and a ligand.
In their single molecule experiments, the team used a new method applying stereographic single molecule force spectroscopy, which is based on atomic force microscopy (AFM). This technique allowed them to study the unbinding of a ligand from a protein bound to a surface not only along a single coordinate, but along all three Cartesian coordinates. During their experiments, Dr. Wanhao Cai, Prof. Dr. Thorsten Hugel and Dr. Bizan N. Balzer of the Institute of Physical Chemistry of the University of Freiburg as well as Dr. Jakob T. Bullerjahn of the Max Planck Institute, made the surprising discovery that friction during ligand unbinding increases with the pulling angle applied.
Combining experiment and computer simulations
Miriam Jäger and Dr. Steffen Wolf of the University of Freiburg’s Institute of Physics subsequently recreated the experiment using computer simulations. They used the high performance computing (HPC) resources of the BinAC-HPC-Cluster in Tübingen. During the simulations they determined that the work of detaching a ligand from its binding site depends on the exact direction of application of the pulling force.
By combining results from the experiment and simulations, the researchers recognized that the source of the angle-dependent friction is the undefinable and random orientation of the proteins along their rotational axes bound to the surface in the experiment. The team repeated the single molecule pulling experiments by binding and unbinding a ligand to and from a protein many times in order to achieve statistically significant results. There, the ligand binds to a different protein for each measurement. Consequently, in each measurement, a ligand was pulled at the same angle with respect to the surface, but over different regions of the randomly-oriented protein. This orientation cannot be defined, both in the experimental setup and in the real world, and each measurement cannot be exactly and reversibly repeated. Therefore, each time different amounts of energy were deposited into the biomolecule. The irreversible part of this energy was lost as heat to the system. The corresponding effect is a source of friction, which the researchers call anisotropic friction.
A fundamental type of friction
“We assume that this previously unknown and fundamental type of friction is present in every bioassembly in which randomness in protein orientation appears together with directionality of force application,” says Dr. Bizan N. Balzer, a biophysicist. He explains that this is the case in biomolecular motors or force-sensitive membrane proteins, as well as for processes such as blood flow, where forces are exerted on randomly oriented proteins. Balzer concludes, “Anisotropic friction is thus another important piece of the puzzle for understanding friction in both technical applications and in biological complexes in general.”
Factual overview:
• Original publication: Cai, W., Jäger, M., Bullerjahn, J. T., Hugel, T., Wolf, S., Balzer, B. N.: Anisotropic Friction in a Ligand-Protein Complex. In: Nano Letters 2023. DOI: http://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.2c04632.
• Thorsten Hugel is a professor, Bizan N. Balzer a lecturer and Wanhao Cai a post-doctoral researcher at the Institute of Physical Chemistry of the University of Freiburg. Hugel and Balzer are members of the Excellence Cluster “Living Adaptive and Energy-autonomous Materials Systems” (livMatS) of the University of Freiburg. Balzer is a member of the Freiburg Materials Research Center (FMF). Steffen Wolf is a lecturer, and Miriam Jäger a doctoral candidate, at the Institute of Physics at the University of Freiburg. They are members of the Research Unit FOR5099 of the German Research Foundation (DFG) “Reducing complexity of nonequilibrium systems.” Jakob T. Bullerjahn is a staff researcher at the Max Planck Institute of Biophysics in Frankfurt-am-Main.
• The German Research Foundation (DFG) is supporting their research through the project HU 997/13-1, the excellence initiative − EXC-2193/1 − 390951807 and the project WO 2410/2-1 within the Research Unit FOR5099 “Reducing complexity of nonequilibrium systems” (project no. 431 945 604) and the project INST 37/935-1 FUGG, as well as the Max Planck Society. Furthermore, the work is being supported by the bwUniCluster-Computing-Initiative, the High Performance/Cloud Computing Group at the Center for Data Processing at the University of Tübingen as well as the state of Baden-Württemberg through bwHPC.
Caption:
Pulling experiments on a biotin-streptavidin complex. Biotin (blue lines) is pulled out of a streptavidin protein (yellow) via a polymer linker (gray line), which is bound to a cantilever tip of an atomic force microscope (gray triangle).
Image source: Dr. Steffen Wolf
Contact:
University and Scientific Communications
University of Freiburg
Tel.: 0761/203-4302
E-Mail: kommunikation@zv.uni-freiburg.de
Weitere Informationen:
https://kommunikation.uni-freiburg.de/pm-en/press-releases-2023/new-type-of-fric…
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Sea slugs inspire highly stretchable biomedical sensor
USC Viterbi School of Engineering researcher Hangbo Zhao presents findings on highly stretchable and customizable microneedles for application in fields including neuroscience, tissue engineering, and wearable bioelectronics. The revolution in…

Twisting and binding matter waves with photons in a cavity
Precisely measuring the energy states of individual atoms has been a historical challenge for physicists due to atomic recoil. When an atom interacts with a photon, the atom “recoils” in…

Nanotubes, nanoparticles, and antibodies detect tiny amounts of fentanyl
New sensor is six orders of magnitude more sensitive than the next best thing. A research team at Pitt led by Alexander Star, a chemistry professor in the Kenneth P. Dietrich…





















