New single-photon Raman lidar can monitor for underwater oil leaks
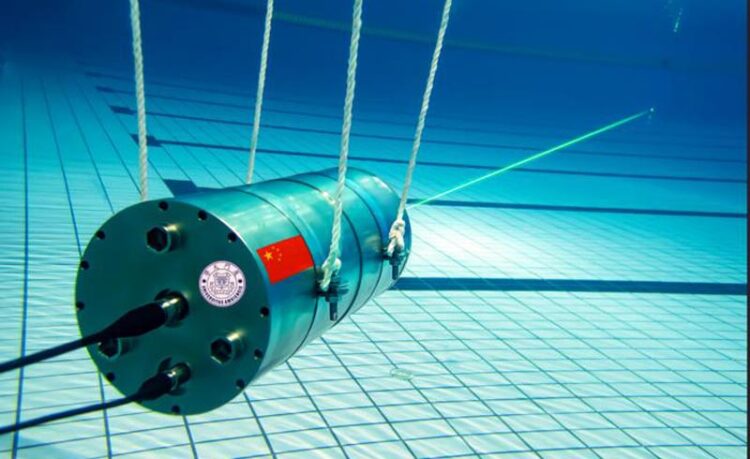
Researchers developed a single-photon Raman lidar system that operates underwater and can remotely distinguish various substances They demonstrated the system by using it to detect varying thicknesses of gasoline oil in a quartz cell that was 12 meters away from the system in a large pool.
Credit: Mingjia Shangguan, Xiamen University
System could be used aboard underwater vehicles for many applications.
Researchers report a new single-photon Raman lidar system that operates underwater and can remotely distinguish various substances. They also show that the new system can detect the thickness of the oil underwater up to 12 m away, which could be useful for detecting oil spills.
“Differentiating substances in water and detecting their distribution characteristics in the ocean are of great significance for marine monitoring and scientific research,” said research team leader Mingjia Shangguan from Xiamen University in China. “For instance, the remote sensing of underwater oil that we demonstrated could be useful for monitoring leaks in underwater oil pipelines.”
Although lidar approaches based on Raman signals have been previously used for detection of underwater substances, existing systems are impractical because they are bulky and require large amounts of power.
In the Optica Publishing Group journal Applied Optics, the researchers describe their new lidar system, which uses just 1 μJ of pulse energy and 22.4 mm of receiver aperture. The entire lidar system is 40 cm long with a diameter of 20 cm and can be operated up to 1 km underwater. To boost sensitivity, the researchers incorporated single-photon detection into their compact underwater Raman lidar system.
“Mounting an underwater Raman lidar system on an autonomous underwater vehicle or remotely operated vehicle could enable monitoring for leaks in underwater oil pipelines,” said Shangguan. “It could potentially also be used to explore oceanic resources or be applied in detecting seafloor sediment types, such as coral reefs.”
Single-photon sensitivity in underwater lidar
Traditional lidar systems designed to operate above water on ships, aircraft or satellites can achieve large-scale ocean profiling, but their detection depth is limited, especially during rough sea conditions. Raman lidar systems, however, can be used for analysis underwater at different depths without being affected by sea conditions.
Raman lidar works by emitting a pulse of green laser light into the water that interacts with substances such as oil. This excites inelastic Raman signals that can be used to identify substances. By measuring the intensity of Raman signals at specific wavelengths, lidar can provide information about the oil content in the water.
“Traditional Raman lidar systems rely on increasing laser power and telescope aperture to achieve remote sensing detection, which leads to a large system size and high-power consumption that make it difficult to integrate lidar systems onto underwater vehicles,” said Shangguan. “The use of single-photon detection technology made this work possible by improving detection sensitivity to the level of single photons.”
The researchers demonstrated their new lidar system by using it to detect varying thicknesses of gasoline oil in a quartz cell that was 12 m away from the system. Both the lidar system and the quartz cell were submerged at a depth of 0.6 m underwater in a large pool. The lidar system was able to detect and distinguish all thicknesses of gasoline, which ranged from 1 mm to 15 mm.
The researchers are now working to increase the number of detection channels and the Raman spectral resolution of the single-photon lidar system to enhance its ability to distinguish different substances in water. This would allow it to be used to analyze underwater bubble types and to detect corals and manganese nodules.
Paper: M. Shangguan, Z. Yang, M. Shangguan, Z. Lin, Z. Liao, Y. Guo, C. Liu, “Remote sensing oil in water with an all-fiber underwater single-photon Raman lidar,” Applied Optics vol. 62 issue 19 pp. 5301-5305 (2023).
DOI: doi.org/10.1364/AO.488872
About Applied Optics
Applied Optics publishes in-depth peer-reviewed content about applications-centered research in optics. These articles cover research in optical technology, photonics, lasers, information processing, sensing and environmental optics. Applied Optics is published three times per month by Optica Publishing Group and overseen by Editor-in-Chief Gisele Bennett, MEPSS LLC. For more information, visit Applied Optics .
About Optica Publishing Group
Optica Publishing Group is a division of Optica (formerly OSA), Advancing Optics and Photonics Worldwide. It publishes the largest collection of peer-reviewed content in optics and photonics, including 18 prestigious journals, the society’s flagship member magazine, and papers from more than 835 conferences, including 6,500+ associated videos. With over 400,000 journal articles, conference papers and videos to search, discover and access, Optica Publishing Group represents the full range of research in the field from around the globe.
Journal: Applied Optics
DOI: 10.1364/AO.488872
Article Title: “Remote sensing oil in water with an all-fiber underwater single-photon Raman lidar
Article Publication Date: 29-Jun-2023
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Why getting in touch with our ‘gerbil brain’ could help machines listen better
Macquarie University researchers have debunked a 75-year-old theory about how humans determine where sounds are coming from, and it could unlock the secret to creating a next generation of more…

Attosecond core-level spectroscopy reveals real-time molecular dynamics
Chemical reactions are complex mechanisms. Many different dynamical processes are involved, affecting both the electrons and the nucleus of the present atoms. Very often the strongly coupled electron and nuclear…

Free-forming organelles help plants adapt to climate change
Scientists uncover how plants “see” shades of light, temperature. Plants’ ability to sense light and temperature, and their ability to adapt to climate change, hinges on free-forming structures in their…