NASA's SDO captures image of mid-level flare
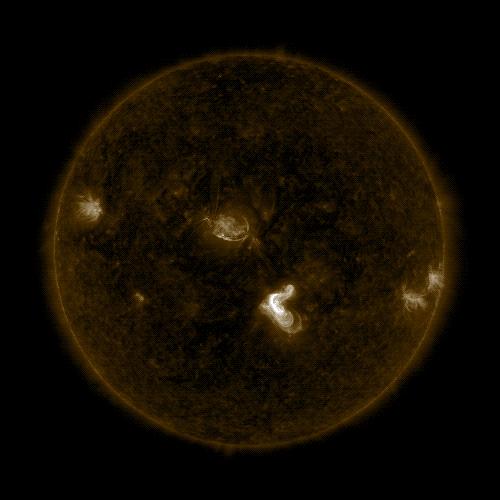

NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory captured this image of a solar flare on Sept. 4, 2017. Credit: NASA/SDO
NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, which watches the sun constantly, captured an image of the event.
Solar flares are powerful bursts of radiation. Harmful radiation from a flare cannot pass through Earth's atmosphere to physically affect humans on the ground, however — when intense enough — they can disturb the atmosphere in the layer where GPS and communications signals travel.
To see how this event may affect Earth, please visit NOAA's Space Weather Prediction Center at http://spaceweather.
This flare is classified as an M5.5 class flare. M-class flares are a tenth the size of the most intense flares, the X-class flares.
The number provides more information about its strength. An M2 is twice as intense as an M1, an M3 is three times as intense, etc.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles
Lower dose of mpox vaccine is safe
… and generates six-week antibody response equivalent to standard regimen. Study highlights need for defined markers of mpox immunity to inform public health use. A dose-sparing intradermal mpox vaccination regimen…

Efficient, sustainable and cost-effective hybrid energy storage system for modern power grids
EU project HyFlow: Over three years of research, the consortium of the EU project HyFlow has successfully developed a highly efficient, sustainable, and cost-effective hybrid energy storage system (HESS) that…

Safer alternative for an explosive reaction
The chemical industry has been using a reaction with explosive chemicals for over 100 years – now Mülheim scientists have discovered a safer alternative. The Ritter Group of the Max…





















