Nanotechnology for energy materials: Electrodes like leaf veins
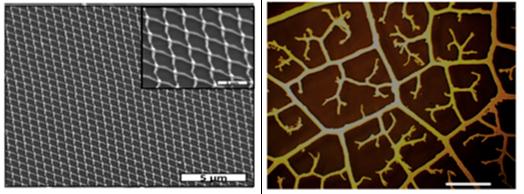
SEM – model of a metallic nano-network with periodic arrangement ( left) and visual representation of a fractal pattern (right). M. Giersig/HZB
An international team headed by HZB scientist Prof. Michael Giersig has recently demonstrated for these applications that networks of metallic mesh possessing fractal-like nano-features surpass other metallic networks in utility. These findings have now been published in the most recent edition of the renowned journal Nature Communications.
Their new development is based on what is termed quasi-fractal nano-features. These structures have similarities to the hierarchical networks of veins in leaves. Giersig’s team was able to show that metallic networks with these features optimise performance of electrodes for several applications.
They combine minimized surface coverage with ultra-low total resistance while maintaining uniform current density. In addition, it was demonstrated that these networks, inspired by nature, can surpass the performance of conventional indium tin oxide (ITO) layers.
In experiments on artificially constructed electrode networks of different topologies, the scientists established that non-periodic hierarchical organisation exhibited lower resistance as well as excellent optical transmittance in comparison to periodic organisation. This led to elevated output power for photovoltaic components.
“On the basis of our studies, we were able to develop an economical transparent metal electrode”, says Giersig, continuing “We obtain this by integrating two silver networks. One silver network is applied with a broad mesh spacing between the micron-diameter main conductors that serve as the “highway” for electrons transporting electrical current over macroscopic distances.”
Next to it, additional randomly distributed nano-wire networks serve as local conductors to cover the surface between the large mesh elements. “These smaller networks act as regional roadways beside the highways to randomise the directions and strengths of the local currents, and also create refraction effects to improve transparency above that of classical shadow-limited performance”, according to Giersig. “Solar cells based upon these electrodes show exceptional a high efficiencies”.
Publication: Optimization of hierarchical structure and nanoscale-enabled plasmonic refraction for window electrodes in photovoltaics; Nature Communications, 7, 12825; doi:10.1038/ncomms12825
additional information:
Prof. Dr. Michael Giersig
E-Mail: giersig@helmhotz-berlin.de
http://www.helmholtz-berlin.de/pubbin/news_seite?nid=14522&sprache=en&ty…
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Recovering phosphorus from sewage sludge ash
Chemical and heat treatment of sewage sludge can recover phosphorus in a process that could help address the problem of diminishing supplies of phosphorus ores. Valuable supplies of phosphorus could…

Efficient, sustainable and cost-effective hybrid energy storage system for modern power grids
EU project HyFlow: Over three years of research, the consortium of the EU project HyFlow has successfully developed a highly efficient, sustainable, and cost-effective hybrid energy storage system (HESS) that…

After 25 years, researchers uncover genetic cause of rare neurological disease
Some families call it a trial of faith. Others just call it a curse. The progressive neurological disease known as spinocerebellar ataxia 4 (SCA4) is a rare condition, but its…





















