More HOPE for the future of disease diagnosis
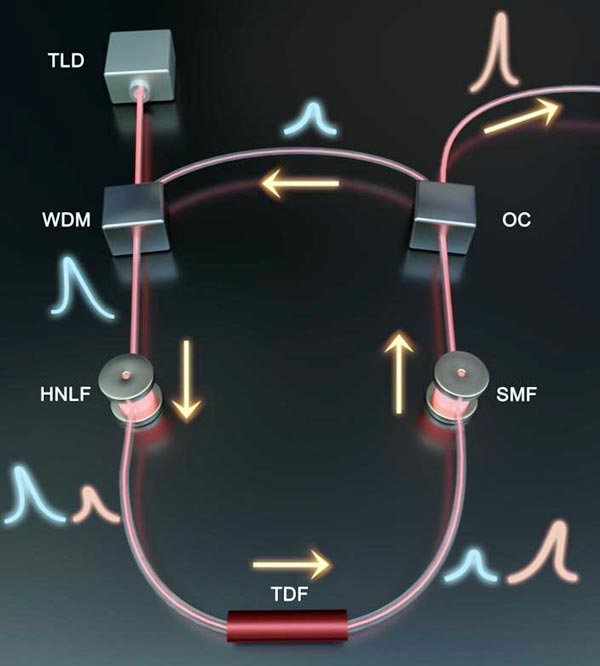
The energy of pump signal at 1.55m band was converted to the idler signal at 1.9m via four-wave mixing (FWM) and then it was amplified by a thulium-doped fiber (TDF) to output.
Credit by Jiawei Shi, Mingsheng Li, Huajun Tang, Jiqiang Kang, Najia Sharmin, Amir Rosenthal, Kenneth K. Y. Wong
Ultrasound images are a powerful biological and biomedical sciences tool. An advancement in this technique is photoacoustic imaging (PAI). It is where the skin or tissue absorbs pulses of laser light. The thermoelastic expansion of the skin or tissue emits sound, which is processed by the machinery to develop high-resolution images. Recent developments have theorized the existence of vibrational PAI, which could penetrate further into the skin.
In a new paper published in eLight, a team of scientists led by Professor Kenneth K. Y. Wong of the University of Hong Kong has developed a high-power hybrid laser emitter designed to penetrate deep into the skin. The paper, titled “Hybrid optical parametrically-oscillating emitter at 1930 nm for volumetric photoacoustic imaging of water content,” sought to map out the water content in the body to analyze the biological properties of cells, tissues, and organs.
The PAI technique needs to generate high-resolution images with a low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). The laser needs to have a high laser pulse energy, fast pulse repetition rate, and accurate wavelength tunability to achieve this goal. Water absorbs energy at a relatively low wavelength of about 1000 nm, which usually requires milli-joule level pulse energy. That sort of energy can burn the skin, while the lasers that operate at that level are expensive.
The research team developed a high-power all-fiber hybrid optical parametrically-oscillating emitter (HOPE) at 1930 nm. It is the best wavelength for determining the water content of tissue and fats. The HOPE emits laser pulses every 15 nanoseconds (ns), with a 1 nm bandwidth. The research team verified the performance of their system through a proof-of-concept optical-resolution PA microscope system.
The team found that the 1930 nm system improved penetration depth by 2.4 mm. The research team owed it to reducing photon scattering in the tissue within the shorter wavelength near-infrared lasers. The improved penetration ability could facilitate measurable imaging of water content in the deep tissue.
Better measuring of water content could improve the quality of medical diagnosis going forward. These excellent advantages could help open broad biological research and disease diagnosis avenues.
Journal: eLight
DOI: 10.1186/s43593-022-00014-2
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Sea slugs inspire highly stretchable biomedical sensor
USC Viterbi School of Engineering researcher Hangbo Zhao presents findings on highly stretchable and customizable microneedles for application in fields including neuroscience, tissue engineering, and wearable bioelectronics. The revolution in…

Twisting and binding matter waves with photons in a cavity
Precisely measuring the energy states of individual atoms has been a historical challenge for physicists due to atomic recoil. When an atom interacts with a photon, the atom “recoils” in…

Nanotubes, nanoparticles, and antibodies detect tiny amounts of fentanyl
New sensor is six orders of magnitude more sensitive than the next best thing. A research team at Pitt led by Alexander Star, a chemistry professor in the Kenneth P. Dietrich…





















