Higher-order topological superconductivity in monolayer Fe(Te,Se)
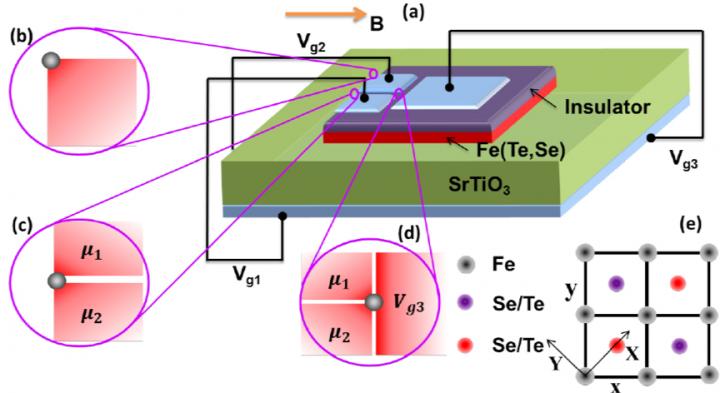
MZMs can be found at three different locations: (b) the corner between two perpendicular edges; (c) the CPDW along the 1D edge; (d) the tri-junction in the 2D bulk. The gray circles in (b), (c) and (d) represent the MZMs, and the magnetic field is in-plane. (e) The crystal structure for the Fe(Te,Se) monolayer.
Credit: @Science China Press
In particle physics, a Majorana Fermion is charge neutral and its antiparticle is just itself. In condensed matter physics, a Majorana zero mode (MZM) is a quasi-particle excitation, which appears in the surfaces or edges of topological superconductors. Unlike the ordinary particles or quasi-particles that obey boson or fermion statistics, MZM obeys non-abelian statistics, a key property that makes MZM the building block for realizing topological quantum computation. Currently major experimental efforts focus on heterostructures made of superconductors and spin-orbit coupled systems (such as semiconducting nano-wires and topological insulators), where evidences of MZMs have been found. Unambiguous detection and manipulation of MZMs in these heterostructures, however, heavily rely on the superconducting proximity effect that suffers from the complexity of the interface. Furthermore, the low operation temperature of conventional superconducting materials complicates further manipulation of MZMs.
Iron-based superconductor was discovered in 2008 by the Japanese scientist Hideo Hosono as the second class of high-Tc materials. In the past decade, intensive studies focused on their unconventional superconductivity and strong correlation effect. Recently, the discovery of topological surface states on the surfaces of iron based superconductor Fe(Te,Se) renders it a unique system integrating both high-Tc superconductivity and topology. Therefore, it provides an exciting opportunity to realize MZM at comparably high critical temperature Tc. Moreover, the monolayer Fe(Te,Se) has a maximum Tc of 40 K and good tenability with a large in-plane upper critical field.
In a study published in Beijing-based National Science Review, a research team led by Chaoxing Liu, an associate professor from Pennsylvania State University, proposed to realize MZMs in monolayer Fe(Te,Se) by applying an in-plane magnetic field and electric gating.
The researchers found that applying an in-plane magnetic field can drive monolayer Fe(Te,Se) into the higher-order topological superconducting phase, in which the MZMs can appear at the corners. Furthermore, through electric gating, MZM can also occur at the domain wall of chemical potentials at one edge and certain type of tri-junction in the two-dimensional bulk (see Figure). According to their estimation, the needed magnetic field is well below the in-plane upper critical magnetic field of monolayer Fe(Te,Se) superconductor. In addition, rotating the magnetic field may provide an efficient approach to perform the braiding operation for the corner MZMs. Therefore, their study demonstrates that monolayer Fe(Te,Se) is a promising Majorana platform with scalability and electrical tunability and within reach of contemporary experimental capability.
###
This research received funding from the Office of Naval Research 330 (Grant No.N00014-18-1-2793), the Kaufman New Initiative research grant of the Pittsburgh Foundation, the German Research Foundation (DFG) through DFG-SFB 1170, project B04 and the Wuerzburg-Dresden Cluster of Excellence on Complexity and Topology in Quantum Matter – ct.qmat (EXC 2147, project-id 39085490).
See the article:
Xianxin Wu, Xin Liu, Ronny Thomale and Chao-Xing Liu
High-Tc superconductor Fe(Se,Te) monolayer: an intrinsic, scalable and electrically tunable Majorana platform
Natl. Sci. Rev. (2021)
https:/
Original Source
http://doi.
Related Journal Article
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Webb captures top of iconic horsehead nebula in unprecedented detail
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has captured the sharpest infrared images to date of a zoomed-in portion of one of the most distinctive objects in our skies, the Horsehead Nebula….

Cost-effective, high-capacity, and cyclable lithium-ion battery cathodes
Charge-recharge cycling of lithium-superrich iron oxide, a cost-effective and high-capacity cathode for new-generation lithium-ion batteries, can be greatly improved by doping with readily available mineral elements. The energy capacity and…

Novel genetic plant regeneration approach
…without the application of phytohormones. Researchers develop a novel plant regeneration approach by modulating the expression of genes that control plant cell differentiation. For ages now, plants have been the…





















