Fermi Arcs in an Antiferromagnet detected at BESSY II
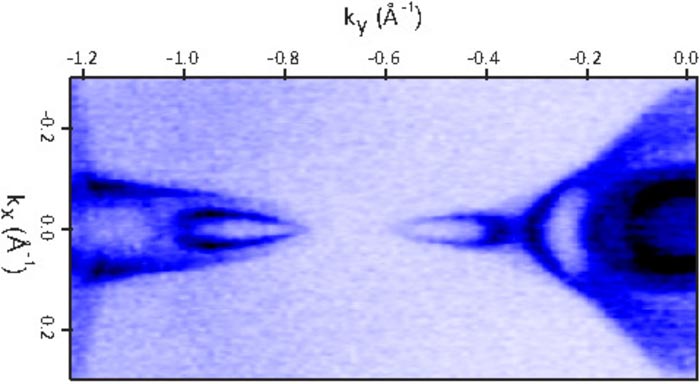
Fermi surface of antiferromagnetic NdBi taken at 6 K temperature at BESSY II. It shows so called Fermi arcs.
Credit: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-022-04412-x
Neodymium-Bismuth crystals belong to the wide range of materials with interesting magnetic properties. The Fermi surface which is measured in the experiments contains information on the transport properties of charge carriers in the crystal.
While usually the Fermi surface consists of closed contours, disconnected sections known as Fermi arcs are very rare and can be signatures of unusual electronic states.
Unusual magnetic splittings
In a study, published now in Nature, the team presents experimental evidence for such Fermi arcs. They observed an unusual magnetic splitting in the antiferromagnetic state of the samples below a temperature of 24 Kelvin (the Néel-temperature).
This splitting creates bands of opposing curvature, which changes with temperature together with the antiferromagnetic order.
These findings are very important because they are fundamentally different from previously theoretically considered and experimentally reported cases of magnetic splittings. In the case of well-known Zeeman and Rashba splittings, the curvature of the bands is always preserved.
Since both splittings are important for spintronics, these new findings could lead to novel applications, especially as the focus of spintronics research is currently moving from traditional ferromagnetic to antiferromagnetic materials.
Journal: Nature
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-04412-x
Method of Research: Experimental study
Subject of Research: Not applicable
Article Title: Emergence of Fermi arcs due to magnetic splitting in an antiferromagnet
Article Publication Date: 23-Mar-2022
COI Statement: none
https://www.helmholtz-berlin.de/pubbin/news_seite?nid=23507&sprache=en&seitenid=1
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Sea slugs inspire highly stretchable biomedical sensor
USC Viterbi School of Engineering researcher Hangbo Zhao presents findings on highly stretchable and customizable microneedles for application in fields including neuroscience, tissue engineering, and wearable bioelectronics. The revolution in…

Twisting and binding matter waves with photons in a cavity
Precisely measuring the energy states of individual atoms has been a historical challenge for physicists due to atomic recoil. When an atom interacts with a photon, the atom “recoils” in…

Nanotubes, nanoparticles, and antibodies detect tiny amounts of fentanyl
New sensor is six orders of magnitude more sensitive than the next best thing. A research team at Pitt led by Alexander Star, a chemistry professor in the Kenneth P. Dietrich…





















