
There is a sound neurological basis for the cliché that men are more aggressive than women, according to new findings by scientists at the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine.
Using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans, the Penn scientists illustrated for the first time that the relative size of the sections of the brain known to constrain aggression and monitor behavior is larger in women than in men.
The research, by Ruben C. Gur, PhD, and Raquel E. Gur, MD, PhD, and

Driven by precise new satellite measurements and sophisticated new computer models, a team of NASA researchers is now routinely producing the first global maps of fine aerosols that distinguish plumes of human-produced particulate pollution from natural aerosols.
In the current issue of the journal Nature, atmospheric scientists Yoram Kaufman, at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md., Didier Tanré and Olivier Boucher from CNRS (Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique)
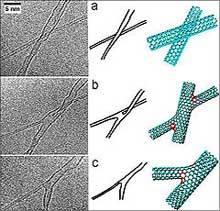
Researchers have discovered how to weld together single-walled carbon nanotubes, pure carbon cylinders with remarkable electronic properties. The discovery could pave the way for controlled fabrication of molecular circuits and nanotube networks.
Pulickel Ajayan, professor of materials science at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute in Troy, N.Y., and his colleagues in Germany, Mexico, the U.K., and Belgium used irradiation and heat to form the welded junctions.
This is the first time

Study shows antioxidant takes no bite out of atherosclerosis in healthy people
LOS ANGELES, Sept. 17-Despite its early promise, taking vitamin E does not appear to slow the progression of atherosclerosis in healthy people, according to researchers from the USC Atherosclerosis Research Unit and colleagues.
Many believe that atherosclerosis, the thickening of artery walls that can lead to heart attack and stroke, results from oxidative damage to tissue in the artery wall cause
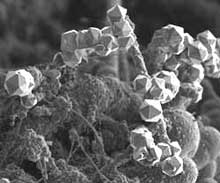
Accident Leads to Important Discovery
Researchers at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute in Troy, N.Y., have created large symmetrical crystals that rarely occur in nature. These crystals could be harder than conventional engineering materials. The accidental discovery was made during attempts to make superconducting nanostructures with a simple technique used to create carbon nanotubes.
Pulickel Ajayan and Ganapathiraman Ramanath, faculty members in materials science and eng

Contrary to popular belief, repetition does not always improve one’s memory for brand claims
Everybody remembers the pink bunny promoting batteries that keep going and going but is it Energizer or Duracell?
Contrary to popular belief in marketing, repetition in advertising does not always improve consumers’ memory for brand claims, says a U of T study. “Consumers often do not absorb the information from ads, so repeating the ads doesn’t necessarily lead to be

NASA’s Coronal Diagnostic Experiment (CODEX) is ready to launch to the International Space Station to reveal new details about the solar wind including its origin and its evolution. Launching in…

In space exploration, long-distance optical links can now be used to transmit images, films and data from space probes to Earth using light. But in order for the signals to…

… in thunderstorm cloud-top corona discharges. A team of researchers from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC), led by Professors LEI Jiuhou, ZHU Baoyou, and Associate Professor…

By applying an electric field, the movement of microswimmers can be manipulated. Scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Dynamics and Self-Organization (MPI-DS), the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Hyderabad…

Researchers at The Jackson Laboratory have developed a new combination of imaging and computational methods to study connections between immune cells in breast cancer and melanoma. A growing cancer is…

Roughly one third of patients with depressive symptoms have elevated levels of inflammation. Inflammation is however often only measured using very broad and unspecific markers. To better understand the connection…

Small drops, big impact: Over time, rain can damage the surfaces of rotor blades. This reduces the efficiency and profitability of wind turbines, especially at sea. Researchers from institutions of…

…takes sensor technology to extreme conditions. Researchers at Tampere University have developed the world’s first soft touchpad that can sense the force, area and location of contact without electricity. The…

Polaritons are coupled excitations of electromagnetic waves with either charged particles or vibrations in the atomic lattice of a given material. They are widely used in nanophotonics because of their…

Researchers discover new magnetic and electronic properties in kagome magnet thin films. A discovery by Rice University physicists and collaborators is unlocking a new understanding of magnetism and electronic interactions…

– Wireless Aggregation of Health Data. Health data, distributed across various applications, could be unified in a digital medical twin: This is how doctors could improve patient care with the…

Large-scale optical programmable logic array can execute complex models like Conway’s Game of Life, marking a significant advancement in optical computing. Researchers have long sought to harness the power of…