Tunneling out of the Surface
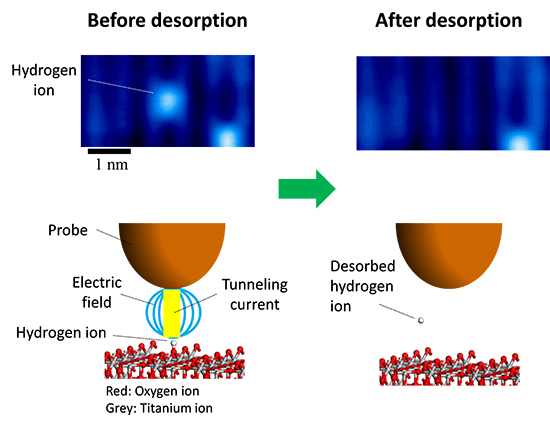
Fig.1: Manipulation of an atomic defect using the probe of a scanning tunneling microscope. Copyright : Tohoku University
The reaction mechanism, reported in ACS Nano, involves the application of an electric field that narrows the width of the reaction barrier, thereby allowing hydrogen atoms to tunnel away from the surface.
This opens the way for the manipulation of the atomic-scale transport channels of hydrogen, which could be important in hydrogen storage. Hydrogen has been put forward as a clean and renewable alternative to the burning of hydrocarbons and one of the great challenges of our day is to find an efficient way to store and transport it.
The team used scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) to directly visualize single hydrogen ions, a common atomic defect on TiO2 (Fig. 1). In STM, the surface structure of a solid surface is observed on the atomic scale by scanning a sharp probe across the surface and monitoring the tunneling current.
Minato et al. were able to desorb individual hydrogen ions from the surface by using the STM probe to apply electrical pulses to the hydrogen.
The pulse generates an electric field as well as injecting electrons into the sample. By using a new theoretical approach developed by Dr. Kajita, the team confirmed that rather than reducing the reaction barrier height, the electric field reduces the width of the barrier, thereby allowing the hydrogen to desorb by quantum tunneling (Fig. 2).
Lead author Prof. Taketoshi Minato (Tohoku Univ. and RIKEN, currently Kyoto University) commented that “The new reaction pathway could be exploited in nanoscale switching devices and hydrogen storage technology. For instance, electric fields could be used to extract hydrogen from a TiO2-based storage device”
Publication Details
Authors:Taketoshi Minato, Seiji Kajita, Chi-Lun Pang, Naoki Asao, Yoshinori Yamamoto, Takashi Nakayama, Maki Kawai, and Yousoo Kim
Title:Tunneling Desorption of Single Hydrogen on the Surface of Titanium Dioxide
Journal:ACS Nano (America Chemical Society)
DOI:10.1021/acsnano.5b01607
Contact:
Professor Taketoshi Minato
International Advanced Research and Education Organization
Office of Society-Academia Collaboration for Innovation
Kyoto University
Email: minato.taketoshi.5xkyoto-u.ac.jp
Tel: +81-774-38-4942
(Formerly of Tohoku University and RIKEN)
Dr. Yousoo Kim
Surface and Interface Science Laboratory, RIKEN
Email: ykimriken.jp
Tel: +81-48‒467‒4073
Professor Maki Kawai
Department of Advanced Materials Science
The University of Tokyo
Email: makik.u-tokyo.ac.jp
Tel: +81-4-7136-3787
Dr. Seiji Kajita
Toyota Central R&D Labs, Inc.
Email: fine-controllermosk.tytlabs.co.jp
Tel: +81-561-71-7258
(Formerly of Chiba University)
Dr. Chi-Lun Pang
Department of Chemistry, University College London
Email: chi.pang@ucl.ac.uk
Tel: +44-207-679-5580
Associated links
Tohoku University article
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.researchsea.comAll latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

Trotting robots reveal emergence of animal gait transitions
A four-legged robot trained with machine learning by EPFL researchers has learned to avoid falls by spontaneously switching between walking, trotting, and pronking – a milestone for roboticists as well…

Innovation promises to prevent power pole-top fires
Engineers in Australia have found a new way to make power-pole insulators resistant to fire and electrical sparking, promising to prevent dangerous pole-top fires and reduce blackouts. Pole-top fires pose…

Possible alternative to antibiotics produced by bacteria
Antibacterial substance from staphylococci discovered with new mechanism of action against natural competitors. Many bacteria produce substances to gain an advantage over competitors in their highly competitive natural environment. Researchers…





















