Scientists have synthesized a new high-temperature superconductor
Scientists have synthesized a new high-temperature superconductor
Credit: Ivan A. Troyan, et.al./Advanced Materials
An international team led by Artem R. Oganov, a Professor at Skoltech and MISIS, and Dr. Ivan Troyan from the Institute of Crystallography of RAS performed theoretical and experimental research on a new high-temperature superconductor, yttrium hydride (YH6). Their findings were published in the journal Advanced Materials.
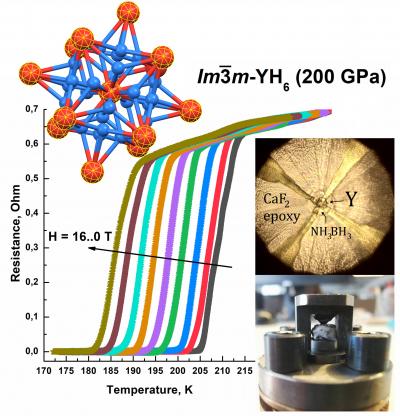
Yttrium hydrides rank among the three highest-temperature superconductors known to date. The leader among the three is a material with an unknown S-C-H composition and superconductivity at 288 K, which is followed by lanthanum hydride, LaH10, superconducting at temperatures up to 259 K), and, finally, yttrium hydrides, YH6 and YH9, with maximum superconductivity temperatures of 224 K and 243 K, respectively. The superconductivity of YH6 was predicted by Chinese scientists in 2015. All of these hydrides reach their maximum superconductivity temperatures at very high pressures: 2.7 million atmospheres for S-C-H and about 1.4-1.7 million atmospheres for LaH10 and YH6. The high pressure requirement remains a major roadblock for quantity production.
“Until 2015, 138 K (or 166 K under pressure) was the record of high-temperature superconductivity. Room-temperature superconductivity, which would have been laughable just five years ago, has become a reality. Right now, the whole point is to attain room-temperature superconductivity at lower pressures,” says Dmitry Semenok, a co-author of the paper and a PhD student at Skoltech.
The highest-temperature superconductors were first predicted in theory and then created and investigated experimentally. When studying new materials, chemists start by making theoretical predictions and then testing new material in practice.
“First, we look at the bigger picture and study a multitude of different materials on the computer. This makes things much faster. More detailed calculations follow the initial screening. Sorting through fifty or a hundred materials takes about a year, while an experiment with a single material of particular interest may last a year or two,” Oganov comments.
Typically, critical superconductivity temperatures are predicted by theory with an error of about 10-15%. Similar accuracy is achieved in critical magnetic field predictions. In the case of YH6, the agreement between theory and experiment is rather poor. For example, the critical magnetic field observed in the experiment is 2 to 2.5 times greater as compared to theoretical predictions. This is the first time scientists encounter such a discrepancy which is yet to be explained. Perhaps, some additional physical effects contribute to this material’s superconductivity and were not accounted for in theoretical calculations.
All latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

Sea slugs inspire highly stretchable biomedical sensor
USC Viterbi School of Engineering researcher Hangbo Zhao presents findings on highly stretchable and customizable microneedles for application in fields including neuroscience, tissue engineering, and wearable bioelectronics. The revolution in…

Twisting and binding matter waves with photons in a cavity
Precisely measuring the energy states of individual atoms has been a historical challenge for physicists due to atomic recoil. When an atom interacts with a photon, the atom “recoils” in…

Nanotubes, nanoparticles, and antibodies detect tiny amounts of fentanyl
New sensor is six orders of magnitude more sensitive than the next best thing. A research team at Pitt led by Alexander Star, a chemistry professor in the Kenneth P. Dietrich…