Scientists develop material that is stable, efficient and eco-friendly
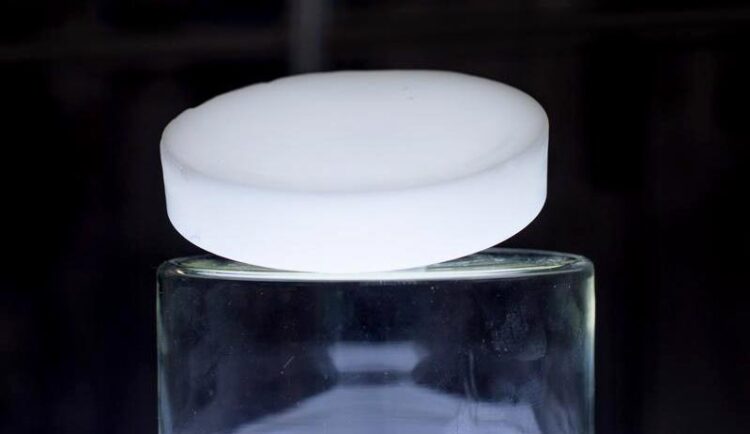

Picture of the new material
Credit: Uni Halle / Marian Sorge
Heat storage:
A new heat storage material could help to significantly improve the energy efficiency of buildings. Developed by researchers at Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) and the University of Leipzig, it can be used to store surplus heat and release it back into the environment when needed. Unlike existing materials, the new one can absorb significantly more heat, is more stable, and is made of harmless substances. In the “Journal of Energy Storage” the team describes the formation mechanism of the material.
The invention is a so-called shape-stabilized phase change material. It can absorb large amounts of heat by changing its physical state from solid to liquid. The stored heat is then re-released when the material hardens. “Many people are familiar with this principle from hand warmers,” explains Professor Thomas Hahn from the Institute of Chemistry at MLU. However, the invention from Halle won’t be used in coat pockets. Instead, it could be used by the construction industry as large panels that could be integrated into walls. These would then absorb heat during the sunny hours of the day and release it again later when the temperature goes down. This could save a lot of energy: The researchers have calculated that when the new material heats up, it can store – under the right conditions – up to 24 times per 10 degrees Celsius more heat than conventional concrete or wallboard.
Unlike hand warmers, the panels made of this material mixture do not melt when they absorb heat. “In our invention, the heat storage material is enclosed in a framework of solid silicate and cannot escape due to high capillary forces,” explains Hahn. Most importantly, the substances used in its production are environmentally friendly: harmless fatty acids like those found in soaps and creams. Even the additives that lend the material its strength and increased thermal conductivity can be obtained from rice husks.
In the current study, the team describes the steps involved in creating the structure of the material and how the different chemicals influence each other. For this, the team received support from a group of researchers led by Professor Kirsten Bacia from MLU, who used fluorescence microscopy to visualise the mechanism. “The knowledge we are gaining can be used to further optimise the material and to potentially produce it on an industrial scale,” says Felix Marske, who drove the development forward as part of his doctorate with Thomas Hahn. Until now the material is still only being produced in small quantities in the laboratory. In the future, it can be combined with other steps to help to make buildings significantly more energy efficient or to passively cool photovoltaic systems and batteries, thereby increasing their efficiency.
Originalpublikation:
Study: Marske F., Dasler J., Haupt C., Bacia K., Hahn T., Enke D. Influence of surfactants and organic polymers on monolithic shape-stabilized phase change materials synthesized via sol-gel route. Journal of Energy Storage (2022). doi: 10.1016/j.est.2022.104127
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2022.104127
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

Sea slugs inspire highly stretchable biomedical sensor
USC Viterbi School of Engineering researcher Hangbo Zhao presents findings on highly stretchable and customizable microneedles for application in fields including neuroscience, tissue engineering, and wearable bioelectronics. The revolution in…

Twisting and binding matter waves with photons in a cavity
Precisely measuring the energy states of individual atoms has been a historical challenge for physicists due to atomic recoil. When an atom interacts with a photon, the atom “recoils” in…

Nanotubes, nanoparticles, and antibodies detect tiny amounts of fentanyl
New sensor is six orders of magnitude more sensitive than the next best thing. A research team at Pitt led by Alexander Star, a chemistry professor in the Kenneth P. Dietrich…