New pop-up strategy inspired by cuts, not folds
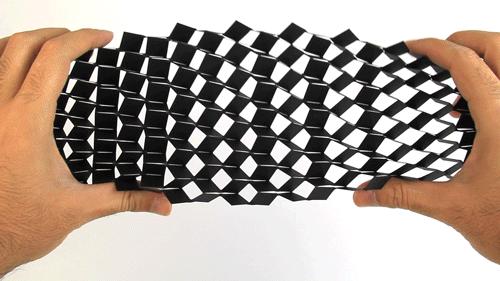
The buckling-induced cubic patterned kirigami sheet can be folded flat. Image courtesy of Ahmad Rafsanjani/Harvard SEAS
Origami-inspired materials use folds in materials to embed powerful functionality. However, all that folding can be pretty labor intensive.
Now, researchers at the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) are drawing material inspiration from another ancient Japanese paper craft — kirigami.
Kirigami relies on cuts, rather than folds, to change the structure and function of materials.
In a new paper published in Physical Review Letters, SEAS researchers demonstrate how a thin, perforated sheet can be transformed into a foldable 3D structure by simply stretching the cut material.
“We find that applying sufficiently large amounts of stretching, buckling is triggered and results in the formation of a 3D structure comprising a well-organized pattern of mountains and valleys, very similar to popular origami folds such as the Miura-ori,” said Ahmad Rafsanjani, a postdoctoral fellow at SEAS and first author of the paper.
The team found that if the material is stretched more, the temporary deformations become permanent folds. The team also found that the pop-up pattern and resulting mechanical properties of the material can be controlled by varying the orientation of the cuts.
“This study shows a robust pop-up strategy to manufacture complex morphable structures out of completely flat perforated sheets,” said Katia Bertoldi, the John L. Loeb Associate Professor of the Natural Sciences at SEAS and senior author of the paper.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

Sea slugs inspire highly stretchable biomedical sensor
USC Viterbi School of Engineering researcher Hangbo Zhao presents findings on highly stretchable and customizable microneedles for application in fields including neuroscience, tissue engineering, and wearable bioelectronics. The revolution in…

Twisting and binding matter waves with photons in a cavity
Precisely measuring the energy states of individual atoms has been a historical challenge for physicists due to atomic recoil. When an atom interacts with a photon, the atom “recoils” in…

Nanotubes, nanoparticles, and antibodies detect tiny amounts of fentanyl
New sensor is six orders of magnitude more sensitive than the next best thing. A research team at Pitt led by Alexander Star, a chemistry professor in the Kenneth P. Dietrich…