How hydrogen behaves in aluminium alloys
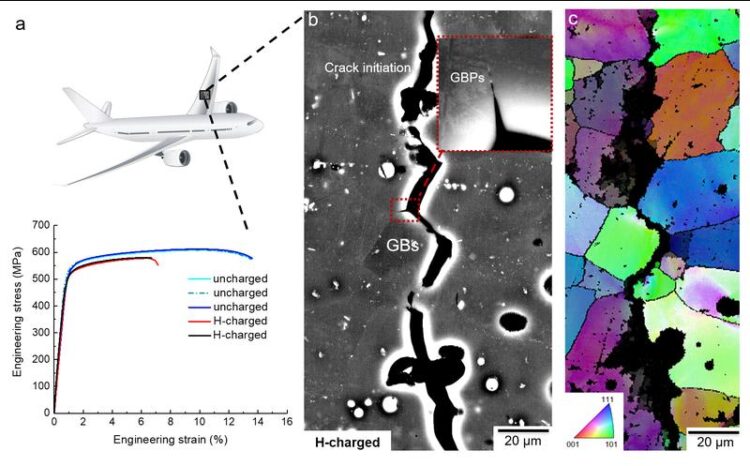
Tensile properties and metallographic fractography of an aluminium-based alloy with zinc, magnesium and copper after aging for 24 hours at 120°C.
Nature, 10.1038/s41586-021-04343-z
Researchers of the Max-Planck-Institut für Eisenforschung publish their latest findings in the journal Nature.
Due to its low density, high strength, and abundance, aluminium and its alloys are widely used for example in constructions, consumer electronics and for vehicles including cars, ships, trains and planes. However, aluminium alloys are prone to hydrogen embrittlement causing catastrophic failure during service if not noticed early enough. Compared to steel, the effects of hydrogen in aluminium are not well understood. Dr. Huan Zhao, postdoctoral researcher at the Max-Planck-Institut für Eisenforschung (MPIE), and her colleagues analysed how hydrogen embrittles aluminium alloys and found first approaches of hindering this effect. The scientists now published their latest results in the journal Nature.
Grain boundaries play a major role in embrittlement effect
“As hydrogen is the smallest of all elements and has low solubility in aluminium, it is extremely challenging to detect on the atomic scale. Whether and how much hydrogen enters aluminium? Where is it located inside the microstructure and how does it affect the properties? All these were unsolved questions till now”, explains Zhao. The MPIE researchers used so-called 7xxx aluminium, a high-strength aluminium class that is the primary material of choice for structural components of airplanes. They charged their samples with hydrogen and performed tensile tests showing that the ductility decreases with increasing amounts of hydrogen.
The fracture surface showed that cracks especially propagated along grain boundaries. Through the cryo-transfer atom probe tomography the scientists revealed that hydrogen gathered along those grain boundaries. “Our experiments were able to show that the amount of hydrogen at particles inside the bulk is much higher than at grain boundaries. However, hydrogen embrittles the material only at the grain boundaries. With the help of computational simulations, we were able to see that hydrogen is attracted by the high energy regions along the grain boundaries causing material’s failure and that particles in the bulk rather act as hydrogen traps, which hinder crack propagation.”, says Dr. Poulami Chakraborty, co-author of the recent publication and postdoctoral researcher at the MPIE.
Intermetallic particles could be a first solution
The MPIE researchers were able to show where hydrogen is located following its ingress during the material’s processing or in service. As this cannot really be prevented, it is important to control its trapping. They recommend different strategies to prevent hydrogen embrittlement, in particular through the use of intermetallic particles that could trap hydrogen inside the bulk material. Additionally, control of the magnesium level at grain boundaries appears critical. “Magnesium paired with hydrogen at grain boundaries increases the embrittlement”, says Zhao. “At the same time, we must manipulate the correct size and volume fraction of particles in the bulk to trap hydrogen while maintaining the material’s strength.” Further studies on the ‘perfect’ particle distribution and eliminating magnesium decoration of grain boundaries are pursued to design advanced high strength, hydrogen-resistant aluminium alloys.
The research was partly funded through the consolidator grant “Shine” of the European Research Council. The project is headed by Prof. Baptiste Gault, group leader at the MPIE and co-author of the recent publication.
Wissenschaftliche Ansprechpartner:
Dr. Huan Zhao, h.zhao@mpie.de
Originalpublikation:
H. Zhao, P. Chakraborty, D. Ponge, T. Hickel, B. Sun, C.H. Wu, B. Gault, D. Raabe: Hydrogen trapping and embrittlement in high-strength Al-alloys. In: Nature, 10.1038/s41586-021-04343-z
Weitere Informationen:
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

Sea slugs inspire highly stretchable biomedical sensor
USC Viterbi School of Engineering researcher Hangbo Zhao presents findings on highly stretchable and customizable microneedles for application in fields including neuroscience, tissue engineering, and wearable bioelectronics. The revolution in…

Twisting and binding matter waves with photons in a cavity
Precisely measuring the energy states of individual atoms has been a historical challenge for physicists due to atomic recoil. When an atom interacts with a photon, the atom “recoils” in…

Nanotubes, nanoparticles, and antibodies detect tiny amounts of fentanyl
New sensor is six orders of magnitude more sensitive than the next best thing. A research team at Pitt led by Alexander Star, a chemistry professor in the Kenneth P. Dietrich…