Zooming in on muscle cells
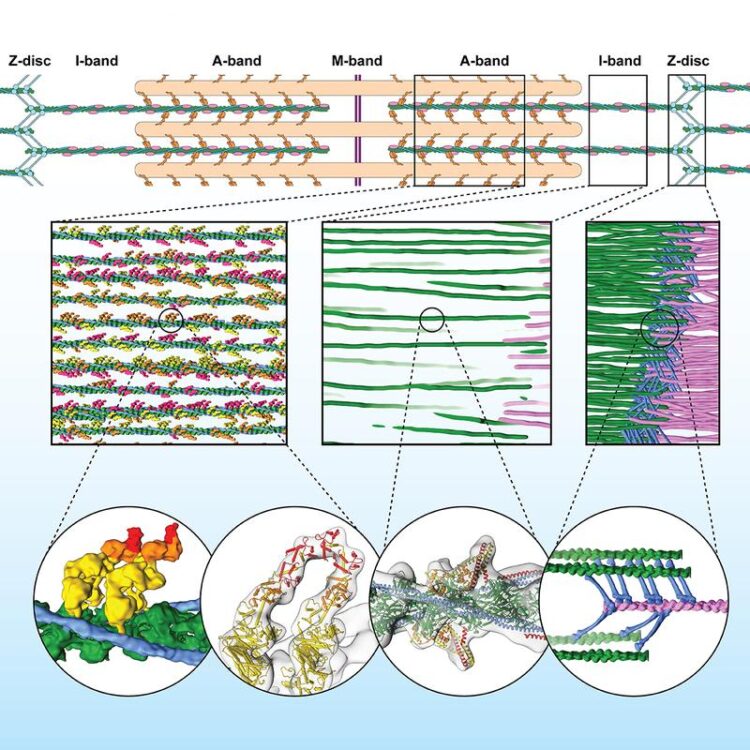
Row 1 shows a schematic representation of the sarcomere. Row 2 shows the three-dimensional sarcomere organization and plasticity at the molecular level (filaments: pink and green, ?-Actinin: blue). Row 3: Interaction of muscle proteins in detail. First two bubbles show the interaction of the myosin heads (yellow, orange, red) with actin (green). Third bubble shows details of actin, tropomyosin and troponin in the A-band. Last bubble depicts irregular mesh of ?-Actinin (blue) cross-linking actin filaments (green, pink) in the Z-disc.
Credit: @MPI of Molecular Physiology
Max Planck Institute’s researchers use electron cryo-tomography to reveal novel molecular details of skeletal sarcomeres.
An old technique flexes its muscles
Sarcomeres are small repeating subunits of myofibrils, the long cylinders that bundle together to make the muscle fibres. Inside the sarcomeres, filaments of the proteins myosin and actin interact to generate muscle contraction and relaxation. So far, traditional experimental approaches to investigate the structure and function of muscle tissue were performed on reconstructed protein complexes or suffered from low resolution. “Electron cryo-tomography, instead, allows us to obtain detailed and artefact-free 3D images of the frozen muscle”, says Raunser.
Cryo-ET was for a long time an established yet niche methodology. But recent technical advances in electron cryo-microscopy (cryo-EM) as well as the new development of cryo focused ion beam (FIB) milling are pushing cryo-ET resolution. Similar to cryo-EM, researchers flash-freeze the biological sample at a very low temperature (- 175 °C). Through this process, the sample preserves its hydration and fine structure and remains close to its native state. FIB milling is then applied to shave away extra material and obtain an ideal thickness of around 100 nanometers for the transmission electron microscope, which acquires multiple images as the sample is tilted along an axis. Finally, computational methods reconstruct a three-dimensional picture at high resolution.
Raunser’s team performed cryo-ET on mouse myofibrils isolated at the King’s College, and obtained a resolution of one nanometer (a millionth of a millimetre, enough to see fine structures within a protein): “We can now look at a myofibril with details thought unimaginable only four years ago. It’s fascinating!”, says Raunser.
Fibres in their natural context
The calculated reconstruction of the myofibrils revealed the three-dimensional organisation of the sarcomere, including the sub regions M-, A-, and I- bands, and the Z-disc, which unexpectedly forms a more irregular mesh and adopts different conformations. The scientists used a sample with myosin strongly bound to actin, representing a stage of the contracting muscle that is called the rigor state. And indeed, they could visualise for the first time in the native cell how two heads of the same myosin bind to an actin filament. They also discovered that the double head not only interacts with the same actin filament but is also found split between two actin filaments. This has never been seen before and shows that proximity to the next actin filament is stronger than the cooperative effect between the neighbouring heads.
“This is just the beginning. Cryo-ET is moving from niche to widespread technology in structural biology”, says Raunser. “Soon we will be able to investigate muscle diseases at molecular and even atomic level”. Mouse muscles are very similar to those of humans, yet scientists plan to investigate muscle tissue from biopsies or derived from pluripotent stem cells.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Sea slugs inspire highly stretchable biomedical sensor
USC Viterbi School of Engineering researcher Hangbo Zhao presents findings on highly stretchable and customizable microneedles for application in fields including neuroscience, tissue engineering, and wearable bioelectronics. The revolution in…

Twisting and binding matter waves with photons in a cavity
Precisely measuring the energy states of individual atoms has been a historical challenge for physicists due to atomic recoil. When an atom interacts with a photon, the atom “recoils” in…

Nanotubes, nanoparticles, and antibodies detect tiny amounts of fentanyl
New sensor is six orders of magnitude more sensitive than the next best thing. A research team at Pitt led by Alexander Star, a chemistry professor in the Kenneth P. Dietrich…





















