UEA research identifies molecules that guide embryonic heart-forming cells
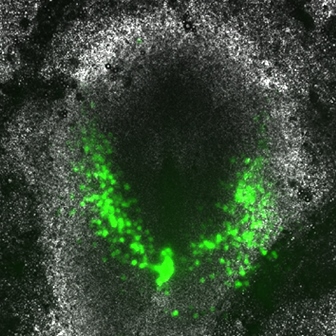
Image above shows an early chick embryo with prospective heart cells labeled in green. These cells are migrating towards the region where they will form the heart.
The heart is the first functioning organ to develop in humans, and correct formation is crucial for embryo survival and growth.
New research published today reveals how cells that form the heart, known as ‘cardiac progenitors’, are guided to move into the right place for the heart to begin to form.
It is hoped that the findings will help researchers better understand how congenital heart defects happen during the early stages of pregnancy.
Researchers studied live chick embryos and used a fluorescent dye to follow how prospective heart cells move together under the microscope.
Lead researcher Prof Andrea Münsterberg, from UEA’s School of Biological Sciences, said: “We have identified two important molecules which work together to control the correct migration of these cells.
They do this by responding to signals, which help the cells navigate their way together – a bit like the embryo’s own GPS system. Once they have arrived in the correct place, they can begin to form the heart.
“Exactly how the cardiac progenitor cells are guided in their movement by these external signals is still unclear, but we have identified two key players that are important in this process.
“This research is particularly important because correct heart formation, at the right time and in the right place, is crucial for embryos to survive and grow.”
The research was funded by British Heart Foundation project grants.
‘Smad1 transcription factor integrates BMP2 and Wnt3a signals in migrating cardiac progenitor cells’ is published in the journal PNAS (Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences) on May 5.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.uea.ac.uk/mac/comm/media/press/2014/may/heart-cellsAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Recovering phosphorus from sewage sludge ash
Chemical and heat treatment of sewage sludge can recover phosphorus in a process that could help address the problem of diminishing supplies of phosphorus ores. Valuable supplies of phosphorus could…

Efficient, sustainable and cost-effective hybrid energy storage system for modern power grids
EU project HyFlow: Over three years of research, the consortium of the EU project HyFlow has successfully developed a highly efficient, sustainable, and cost-effective hybrid energy storage system (HESS) that…

After 25 years, researchers uncover genetic cause of rare neurological disease
Some families call it a trial of faith. Others just call it a curse. The progressive neurological disease known as spinocerebellar ataxia 4 (SCA4) is a rare condition, but its…





















