Toward Methuselah – Long-Living Lighting Devices
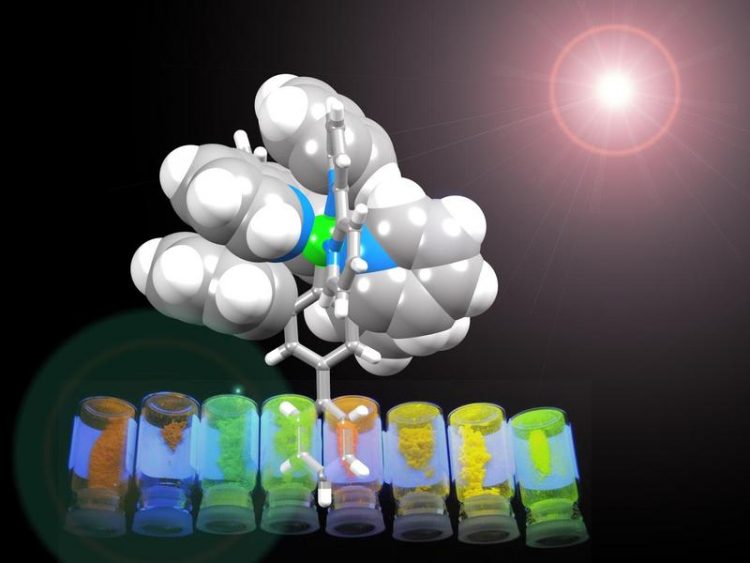
The iridium metal center is wrapped in an organic coat which protects it in the LEC. © University of Basel
Lighting technology is in a state of change. The old-fashioned light-bulb, which was more efficient at converting electricity into heat than light, is currently being replaced by fluorescent devices and it is expected that light emitting diodes (LEDs) will be the technology of choice in the mid-term future.
The research group lead by Basel professors Catherine E. Housecroft and Edwin C. Constable describes the design of new molecular components and strategies for the preparation of light-emitting electrochemical cells (LECs) with remarkable lifetimes.
Simpler and less demanding LECs
LEDs have the disadvantage that they are complex, multilayered devices that require high-vacuum and high temperature techniques for their preparation. They also need to be rigorously protected from exposure to air or water. LECs are much simpler devices, comprising only one layer of active material, which can be solution-processed in ambient conditions.
To date, LEC devices have had relatively short lifetimes which have precluded serious commercial investigation. The Basel and Valencia teams have shown that devices with lifetimes exceeding 2500 hours can now be prepared using molecular components stabilized by so-called aromatic rings.
The team has built metal complexes decorated with rings that arrange themselves to form a shell around the molecule. “It is a little bit like a flower closing up at night – the flat, petal-like rings fold up about the metal to make a compact and robust structure”, says Constable.
These supramolecular interactions make the complexes exceptionally stable. Furthermore, molecular tuning of the components allows a tuning of the color of light emitted, bringing the goal of white-light emitting devices one step closer.
Original source
Andreas M. Bünzli, Edwin C. Constable, Catherine E. Housecroft, Alessandro Prescimone, Jennifer A. Zampese, Giulia Longo, Lidón Gil-Escrig, Antonio Pertegás, Enrique Ortí and Henk J. Bolink
Exceptionally long-lived light-emitting electrochemical cells: multiple intra-cation π-stacking interactions in [Ir(C^N)2(N^N)][PF6] emitters
Chem. Sci., 2015, 1-10 | doi: 10.1039/c4sc03942d
Further information
Edwin C. Constable, Department of Chemistry, University of Basel, Tel. +41 61 267 10 01, Email: edwin.constable@unibas.ch
Catherine E. Housecroft, Department of Chemistry, University of Basel, Tel. +41 61 267 10 08, Email: catherine.housecroft@unibas.ch
https://www.unibas.ch/en/News-Events/News/Uni-Research/Long-Living-Lighting-Devi…
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.unibas.chAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Webb captures top of iconic horsehead nebula in unprecedented detail
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has captured the sharpest infrared images to date of a zoomed-in portion of one of the most distinctive objects in our skies, the Horsehead Nebula….

Cost-effective, high-capacity, and cyclable lithium-ion battery cathodes
Charge-recharge cycling of lithium-superrich iron oxide, a cost-effective and high-capacity cathode for new-generation lithium-ion batteries, can be greatly improved by doping with readily available mineral elements. The energy capacity and…

Novel genetic plant regeneration approach
…without the application of phytohormones. Researchers develop a novel plant regeneration approach by modulating the expression of genes that control plant cell differentiation. For ages now, plants have been the…





















