Single-atom tractor beams power chemical catalysis
Single-atom tractor beams power chemical catalysis
Credit: Research Team, Cavendish Laboratory, Department of Physics, University of Cambridge
Unlocking possible new ways to make light act powerfully and drive chemical transformations.
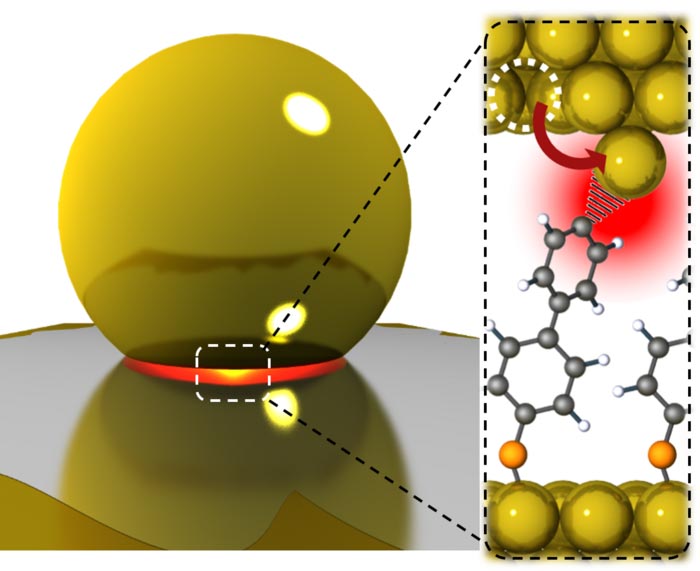
By trapping light into tiny gaps only a few atoms wide, a team from the NanoPhotonics Centre has magnified optical forces a thousand-fold, strong enough to force atoms into positions that drive chemical reactions more efficiently.
“We found a new way to beef up the forces from light, enough to now move metal atoms, and that’s key to reduce the energy barrier for making catalysis work more easily” co-lead researcher Shu Hu explains.
Weak tractor beams are used to make optical tweezers that can probe biological processes with beams of tightly-focussed light that trap transparent micro-objects of glass or polymer. But to use light to pluck single atoms from solids requires much stronger forces. Now a team from the NanoPhotonics Centre in the Cavendish Laboratory has shown a way to build tiny crevices that magnify the optical forces of visible light. They use these to pull single gold atoms from a crystal, approach them close to a molecular bond, and watch the effects directly on their flopping and vibration. Published in Science Advances , they show new ways to make light act powerfully, and suggest new approaches for driving chemical transformations.
Watching one bond at a time in their experiments avoids averaging over a crowd of different effects. “Single metal atoms are the anvil where catalysis forges new chemical bonds” promises Prof Jeremy Baumberg, “and we can start to watch this process happening and control it”. Catalysis is instrumental for all manmade chemicals and polymers.
“It’s like watching the beautiful dance of an atom and a molecule in real time” notes Hu.
Reference: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.abp9285
Jeremy J. Baumberg, Shu Hu et al. ‘ Optical suppression of energy barriers in single molecule-metal binding’ Science Advances. DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abp9285
Media Contact
Pooja Pandey
University of Cambridge
pp550@cam.ac.uk
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Sea slugs inspire highly stretchable biomedical sensor
USC Viterbi School of Engineering researcher Hangbo Zhao presents findings on highly stretchable and customizable microneedles for application in fields including neuroscience, tissue engineering, and wearable bioelectronics. The revolution in…

Twisting and binding matter waves with photons in a cavity
Precisely measuring the energy states of individual atoms has been a historical challenge for physicists due to atomic recoil. When an atom interacts with a photon, the atom “recoils” in…

Nanotubes, nanoparticles, and antibodies detect tiny amounts of fentanyl
New sensor is six orders of magnitude more sensitive than the next best thing. A research team at Pitt led by Alexander Star, a chemistry professor in the Kenneth P. Dietrich…





















