Natural anti-freeze – how arthropods survive the cold

Arthropods face much the same dilemma, as they cannot migrate long distances to avoid low winter temperatures – so why are they not killed off by the cold? Dr Melody Clark, from the British Antarctic Survey, will present data on the fascinating ways two species of these animals combat the cold on Tuesday 3rd April at the Society for Experimental Biology’s Annual Meeting in Glasgow.
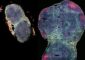
Onychiurus arcticus (from the Arctic) uses protective dehydration to survive harsh Arctic winters. This means that water is lost from the body across a diffusion gradient between the animals’ super-cooled body fluids and ice in the surroundings. “During this process the body loses all its water and you end up with a normal looking head, and a body which looks like a crumpled up crisp packet when it is fully dehydrated. But add a drop of water and it all goes back to normal!” explains Dr Clark. Scientists examined the different stages of this process to see which genes were activated.
Cryptopygus antarcticus lives in the Antarctic and uses a different mechanism to survive cold temperatures. These creatures accumulate anti-freeze compounds which lower the temperature at which their bodies freeze, meaning they can withstand temperatures as low as minus 30°C. Within this population there is a clear divide into less- and more-cold hardened animals, which has been a puzzle to researchers. However, by looking for differences in gene expression levels between the two populations, scientists think that there could be a link to moulting (this is the process by which arthropods shed their exoskelton).
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.sebiology.org.uk/Meetings/pageview.asp?S=2&mid=&id=738All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles
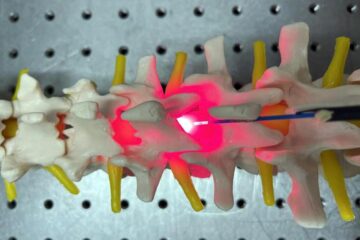
Red light therapy for repairing spinal cord injury passes milestone
Patients with spinal cord injury (SCI) could benefit from a future treatment to repair nerve connections using red and near-infrared light. The method, invented by scientists at the University of…

Insect research is revolutionized by technology
New technologies can revolutionise insect research and environmental monitoring. By using DNA, images, sounds and flight patterns analysed by AI, it’s possible to gain new insights into the world of…

X-ray satellite XMM-newton sees ‘space clover’ in a new light
Astronomers have discovered enormous circular radio features of unknown origin around some galaxies. Now, new observations of one dubbed the Cloverleaf suggest it was created by clashing groups of galaxies….