New Ribozyme for Exploring the World of RNA
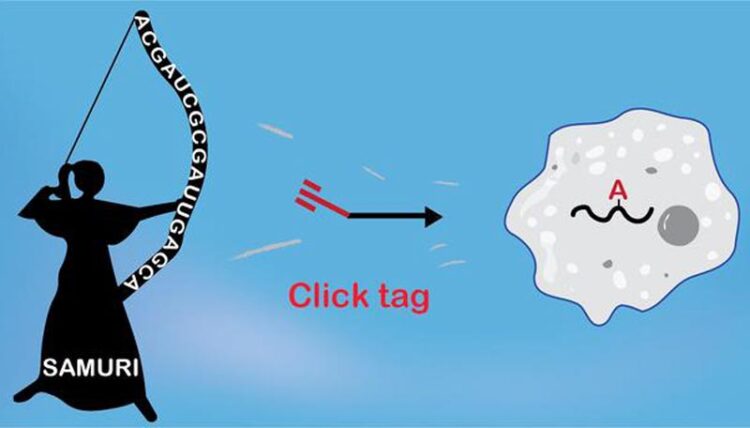
SAMURI is a new ribozyme that attaches a targeted modification to cellular RNA for click chemistry. (Image: Arbeitsgruppe Claudia Höbartner / Universität Würzburg)
Important progress for RNA research: A team led by Würzburg chemistry professor Claudia Höbartner has discovered a new ribozyme that can label RNA molecules in living cells.
RNA molecules are real all-rounders. They transfer the genetic information from the DNA in the cell. They regulate the activity of genes. And some of them have a catalytic effect: just like enzymes, they enable biochemical reactions that would be difficult or impossible to occur on their own. These special RNA molecules that accelerate such reactions are called ribozymes.
The team of chemistry professor Claudia Höbartner from Julius-Maximilians-Universität (JMU) Würzburg now presents a newly discovered ribozyme called SAMURI in the journal Nature Chemistry.
SAMURI can precisely modify other RNA molecules. This ability is very helpful for RNA research: “We can use such ribozymes as tools to label RNA with dyes and make it visible,” says JMU researcher Dr. Takumi Okuda. “In this way, the pathways of RNA in the cell and its interactions with other molecules can be studied even better.”
Ribozymes may also be considered for therapeutic use in the future. “We see new possible applications for ribozymes when the enzymes responsible for a specific task are missing or are no longer functional due to mutations,” says Claudia Höbartner.
Details about the new ribozyme
What distinguishes the new ribozyme SAMURI? It modifies other RNA molecules at a precisely defined site of a specific adenine. There it attaches molecules to which, in turn, dyes or other molecules can easily be clicked in – like buckling up a seat belt. Such reactions are known as click chemistry.
SAMURI also has the advantage that it is active under the same physiological conditions that prevail in living cells. This is not the case with other synthetic ribozymes.
Another special feature: SAMURI uses a new synthetic cofactor to make RNA molecules accessible for click chemistry. This cofactor was developed by Dr. Takumi Okuda; it was inspired by the ubiquitous natural cofactor SAM (S-adenosylmethionine). This is also where the name of the new ribozyme comes from: SAMURI stands for “SAM-analogue utilising ribozyme”.
The following steps in research
Claudia Höbartner’s group next wants to elucidate the structure and mechanism of action of SAMURI. She also wants to develop further ribozymes that can modify RNA building blocks other than adenine.
Cooperation partners and sponsors
The publication was produced in cooperation with the research group of Professor Jörg Vogel, head of the Würzburg Helmholtz Institute for RNA-based Infection Research (HIRI) and head of the JMU Chair of Molecular Infection Biology I. Financial support came from the German Research Foundation (DFG) and the European Research Council (ERC).
The Chair of Organic Chemistry I
Headed by Professor Claudia Höbartner, the Chair of Organic Chemistry I at Julius-Maximilians-Universität (JMU) Würzburg explores the chemistry of nucleic acids. The group synthesises chemically modified DNA and RNA; it develops DNA catalysts, ribozymes and RNA aptamers. The team investigates the functions of these biomolecules and develops innovative applications at the interface of chemistry and molecular biology.
Wissenschaftliche Ansprechpartner:
Prof. Dr. Claudia Höbartner, Head of the Chair of Organic Chemistry I, University of Würzburg, claudia.hoebartner@uni-wuerzburg.de
Originalpublikation:
A SAM analogue-utilising ribozyme for site-specific RNA alkylation in living cells, Nature Chemistry, 4 September 2023, DOI: 10.1038/s41557-023-01320-z
Weitere Informationen:
https://www.chemie.uni-wuerzburg.de/oc/hoebartner-group Website Hoebartner group
https://www.uni-wuerzburg.de/en/news-and-events/news/detail/news/ribozyme-samuri/
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles
Economies take off with new airports
A global study by an SUTD researcher in collaboration with scientists from Japan explores the economic benefits of airport investment in emerging economies using nighttime satellite imagery. Be it for…
CAR T–cell immunotherapy targets
Pan-cancer analysis uncovers a new class of promising CAR T–cell immunotherapy targets. Scientists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital found 156 potential CAR targets across the brain and solid tumors,…

Stony coral tissue loss disease
… is shifting the ecological balance of Caribbean reefs. The outbreak of a deadly disease called stony coral tissue loss disease is destroying susceptible species of coral in the Caribbean…





















