Innovative catalysts: An expert review
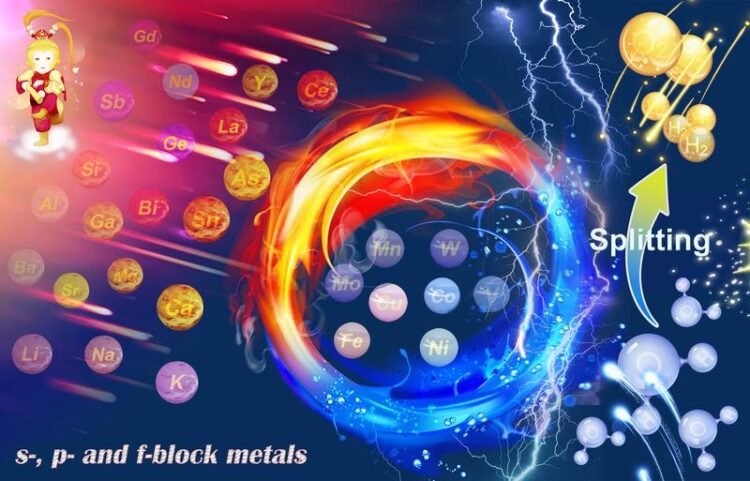
With the help of innovative elctrocatalytic materials, water can be split up into oxygen and hydrogen. Hydrogen is a fuel storing chemical energy as long as needed
Credit: Dr. Ziliang Chen
Green hydrogen is an important component in a climate-neutral energy system. It is produced by electrolytically splitting water with wind or solar power and stores this energy in chemical form. But currently, the production of green hydrogen is not yet economical or efficient enough. The key to solving this problem is through the development of innovative electrocatalysts, which should not only work with high efficiencies but should also be available and inexpensive.
In addition to transition metals, which are already well studied for their catalytic properties, a wider choice of elements has now moved into the focus such as alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, rare earth metals, lean metals and metalloids. Some of these when combined with transition metal electrocatalysts can significantly improve performance and contribute to the development of next-generation high-performance electrocatalysts.
However, many of the processes that take place during electrocatalysis -when oxygen or hydrogen is formed – are still not understood in detail. In a review article, an international team of experts guides us through this exciting research field and draws a perspective, sketching the next steps catalyst research could take. “This contribution summarises the current state of knowledge on such unconventional s-, p-, and f-block metal-based materials and makes it comprehensible to a wider community of scientists”, Dr. Prashanth W. Menezes points out and adds: “Further, the essential role of such metals during water splitting electrocatalysis is described in great depth, as well as the modification strategy that should be considered when one wants to utilize them to mediate non-noble-based electrocatalysts. We hope to significantly accelerate research and development of novel, innovative catalyst materials with this review article.”
Note: Dr. Prashanth W. Menezes is Head of Materials Chemistry for Thin-Film Catalysis Group in the CatLab-Project at HZB and Head of Inorganic Materials Group at TU Berlin.
His twitterhandle is @EnergycatLab
CatLab: Together with the Fritz Haber Institute of the Max Planck Society, HZB is setting up the Catalysis Laboratory CatLab, which is intended to accelerate research into innovative catalysts. CatLab is supported by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research.
https://www.helmholtz-berlin.de/projects/catlab/index_en.html
Journal: Advanced Materials DOI: 10.1002/adma.202108432 Method of Research: Systematic review Subject of Research: Not applicable Article Title: The Pivotal Role of s-, d-, and f-Block Metals in Water Electrolysis: Status Quo and Perspectives Article Publication Date: 1-Feb-2022 COI Statement: none
Media Contact
Antonia Roetger
Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin für Materialien und Energie
antonia.roetger@helmholtz-berlin.de
Office: 0049-308-062-43733
Original Source
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Webb captures top of iconic horsehead nebula in unprecedented detail
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has captured the sharpest infrared images to date of a zoomed-in portion of one of the most distinctive objects in our skies, the Horsehead Nebula….

Cost-effective, high-capacity, and cyclable lithium-ion battery cathodes
Charge-recharge cycling of lithium-superrich iron oxide, a cost-effective and high-capacity cathode for new-generation lithium-ion batteries, can be greatly improved by doping with readily available mineral elements. The energy capacity and…

Novel genetic plant regeneration approach
…without the application of phytohormones. Researchers develop a novel plant regeneration approach by modulating the expression of genes that control plant cell differentiation. For ages now, plants have been the…





















