Hijacking bacteria's natural defences to trap and reveal pathogens
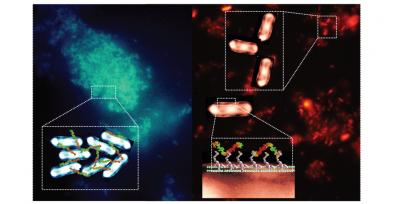
The image shows a) on the left hand side, aggregates of E coli labelled blue by in situ activated polymers, and b) on the right hand side E. coli clusters in suspension with bacterial-instructed polymers Schematics of the binding process are shown in the enlargement boxes of the image. Credit: Professor Cameron Alexander The University of Nottingham UK
The research was led by Professor Cameron Alexander, Head of the Division of Drug Delivery and Tissue Engineering and EPSRC Leadership Fellow in the University's School of Pharmacy, building on work by PhD student Peter Magennis.
Professor Alexander said: “Essentially, we have hijacked some of the metabolic machinery which bacteria use to control their environment, and used it instead to grow polymers which bind strongly to the specific bacteria that produce them.
“The neat thing about this is that the functionality of the polymers grown on the surface of the bacteria is programmed by the cells so that they can recognise their own 'kind'. We used fluorescent labels to light up the polymers and were able to capture this labelling using a mobile phone camera, so in principle it could be possible to use these materials as point-of-care diagnostics for pathogenic bacteria.”
The study has shown that the bacteria helped to synthesise polymers on their own surfaces which not only were different from those made by conventional methods, but which retained a form of 'structural memory' of that surface. This means in future it should be possible to make specific detection agents or additives for topical anti-infectives that target a number of harmful bacteria all by a common route.
“The initial focus of the research was to explore ways to use synthetic polymers to selectively target and bind the bacteria that cause dental cavities and periodontal diseases in order to facilitate their removal from the oral cavity,” said Dr David Churchley, Principal Scientist, Oral Health Category Research and Development, GSK Consumer Healthcare. “As we continued our work, we saw that our research had broader implications and potential for a wider range of uses.”
Rapidly identifying harmful bacteria at the heart of a serious medical or dental condition can be a difficult and costly task. The group's findings may even lead to new ways of treating bacterial infections. “These types of polymers may be designed to contain antibacterial functionalities so that they specifically bind to and kill bacterial pathogens,” said Dr Klaus Winzer, a microbiologist at The University of Nottingham involved in the study. The selective binding of specific bacterial species and/or strains in current practice requires expensive 'cold-chain' reagents such as antibodies which often preclude using these processes outside of a hospital setting or in developing nations.
The new approach, termed 'bacterial-instructed synthesis', has the potential for use in the developing world, in the field or in less specialised laboratory settings.
Dr David Bradshaw, Principal Scientist, Oral Health Category Research and Development, GSK Consumer Healthcare, said: “The ingredients used to form the polymers are all easy to obtain, inexpensive and widely available. With the simplicity and accessibility of the chemistry, a number of diagnostic and other applications may be possible.”
The study was funded by a Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC) GSK Consumer Healthcare CASE studentship, and Professor Alexander's Engineering and Physical Research Council (EPSRC) Leadership Fellowship.
The paper will be accessible on the Nature Materials website (after the embargo has lifted) at http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nmat3949
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Webb captures top of iconic horsehead nebula in unprecedented detail
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has captured the sharpest infrared images to date of a zoomed-in portion of one of the most distinctive objects in our skies, the Horsehead Nebula….

Cost-effective, high-capacity, and cyclable lithium-ion battery cathodes
Charge-recharge cycling of lithium-superrich iron oxide, a cost-effective and high-capacity cathode for new-generation lithium-ion batteries, can be greatly improved by doping with readily available mineral elements. The energy capacity and…

Novel genetic plant regeneration approach
…without the application of phytohormones. Researchers develop a novel plant regeneration approach by modulating the expression of genes that control plant cell differentiation. For ages now, plants have been the…





















