Advancing the generation of in-vivo chimeric lungs in mice
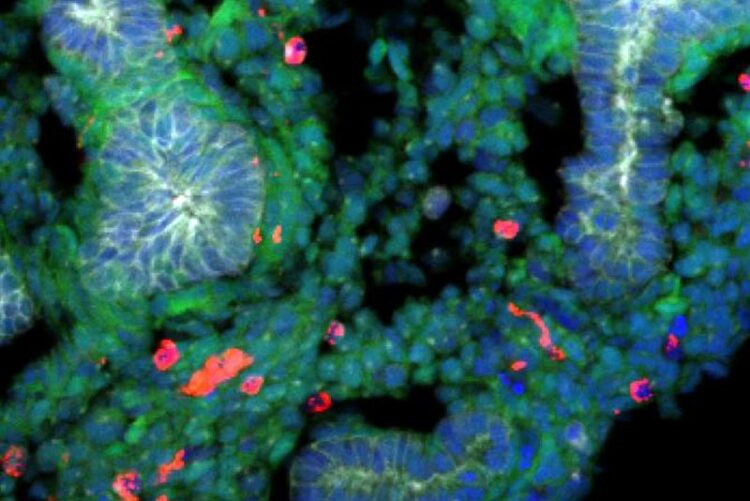
A rat embryonic stem cells derived lung generated within a mouse body stained with epithelial cells (labelled with E-cadherin, shown in gray), rat cells (shown in green), mouse cells (shown in red), and DNA (labelled with Hoechst, shown in blue). Rat cells are predominantly detected in the lung, and the epithelial tissues are exclusively composed of rat cells.
Credit: Shunsuke Yuri
… using rat-derived stem cells.
Researchers from Japan explore the conditions needed for organ regeneration and overcoming species-specific barriers to create functional organs in interspecies chimeric animals.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is the third leading cause of death worldwide. It is marked by lung damage that is lasting and incurable, leaving lung transplantation as the only viable treatment option. Unfortunately, finding suitable lung donors is difficult. To compensate for this shortage of donors, regenerative medicine is making strides in developing lungs from pluripotent stem cells (PSCs), using interspecies animal models.
Through a biological technique known as blastocyst complementation, PSCs, and embryonic stem cells (ESCs) from one species can be injected into blastocysts of a different organ-deficient species, creating interspecies chimeric animals. This technique has enabled successful regeneration of the pancreas, heart, and kidney in rat-mouse chimeras. However, functional lung formation has still not been achieved successfully, warranting further research into the viable conditions required to generate PSC-derived organs.
Now, scientists from Nara Institute of Science and Technology (NAIST), Japan have used the reverse-blastocyst complementation (rBC) method to understand the conditions required to form lungs in rat-mouse chimeric models. In addition, they used the tetraploid-based organ complementation (TOC) method to successfully create a rat-derived lung in their mouse model. The study, published in Development, was led by Shunsuke Yuri and Ayako Isotani from NAIST.
The fibroblast growth factor 10 (Fgf10) and its interaction with the Fgf receptor 2 isoform IIIb (Fgfr2b) in the lungs are crucial for lung development. In this study, the rBC method involved injecting mutant ESCs which fail to show lung formation into wild-type (WT) embryos. This method allows for efficient detection of mutant PSCs in the recipient tissue, aiding the determination of the conditions necessary for successful lung formation in the organ-deficient animal.
The research team also found that WT ESCs provide uniform contributions across target and non-target organs in the chimeras. This helped ascertain that a certain number of WT or normal cells are required to overcome the lung development failure in Fgf10-deficient or Fgfr2b-deficient animals.
With this knowledge, they successfully produced rat-derived lungs in the Fgfr2b-deficient mouse embryos with the TOC method, without needing to produce a mutant mouse line. “Interestingly, we found that the rat epithelial cells conserved intrinsic species-specific timing in the interspecies model, resulting in an underdeveloped lung,” notes Yuri. Consequently, these lungs remained nonfunctional post-birth.
The findings of this study clearly identify the factors required and barriers to overcome for successful generation of functional lungs in rat-mouse interspecies chimeras. Speaking of the significance of these findings, Yuri concludes, “We believe that our study makes an important contribution to the literature by presenting a faster and more efficient method of exploring blastocyst complementation. These novel results can significantly advance the progress toward developing in-vivo chimeric lungs for the purpose of transplantation, which could transform the practical application of regenerative medicine.”
Resource
Title: Generation of rat-derived lung epithelial cells in Fgfr2b-deficient mice retains species-specific development
Authors: Shunsuke Yuri, Yuki Murase, Ayako Isotani
Journal: Development
DOI: 10.1242/dev.202081
More information about the Organ Developmental Engineering Lab can be found at the following website: https://bsw3.naist.jp/eng/courses/courses214.html
About Nara Institute of Science and Technology (NAIST)
Established in 1991, Nara Institute of Science and Technology (NAIST) is a national university located in Kansai Science City, Japan. In 2018, NAIST underwent an organizational transformation to promote and continue interdisciplinary research in the fields of biological sciences, materials science, and information science. Known as one of the most prestigious research institutions in Japan, NAIST lays a strong emphasis on integrated research and collaborative co-creation with diverse stakeholders. NAIST envisions conducting cutting-edge research in frontier areas and training students to become tomorrow’s leaders in science and technology.
Journal: Development
DOI: 10.1242/dev.202081
Article Title: Generation of rat-derived lung epithelial cells in Fgfr2b-deficient mice retains species-specific development
Media Contact
Takahito Shikano
Nara Institute of Science and Technology
press_contact@rsc.naist.jp
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Possible alternative to antibiotics produced by bacteria
Antibacterial substance from staphylococci discovered with new mechanism of action against natural competitors. Many bacteria produce substances to gain an advantage over competitors in their highly competitive natural environment. Researchers…

Researchers have found brown fat’s “off-switch
Researchers from the University of Southern Denmark, the Novo Nordisk Center for Adipocyte Signaling (SDU), the University of Bonn and the University Hospital Bonn (UKB) have found a protein that…

Combining robotics and ChatGPT
TUM professor uses ChatGPT for choreographies with flying robots. Prof. Angela Schoellig has proved that large language models can be used safely in robotics. ChatGPT develops choreographies for up to…





















