3-D protein structure offers insight into rapid communication by brain cells
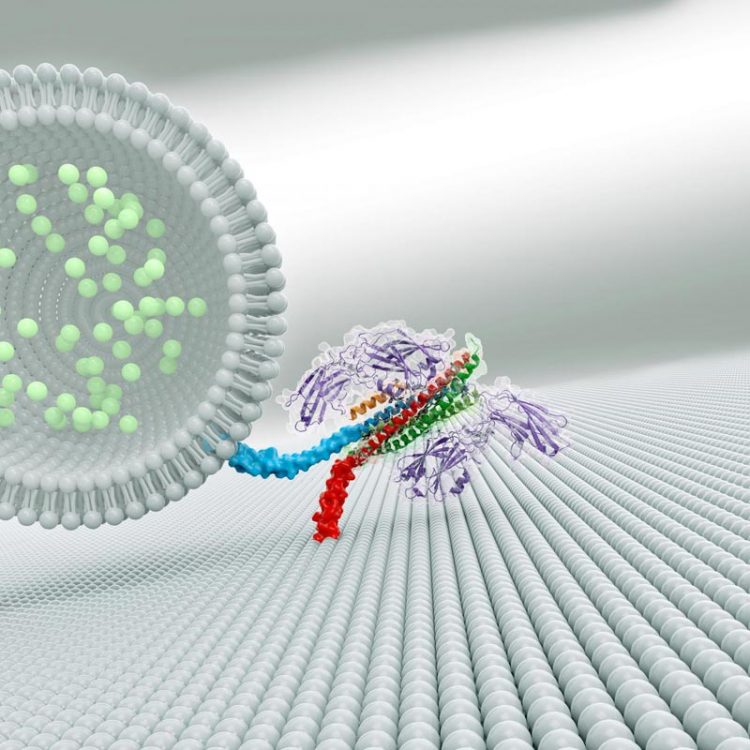
A complex of three proteins (shown at right in this artistic rendering) helps brain cells quickly release neurotransmitters (light green) to communicate with neighboring cells. Credit: Zhou et al./ Nature 2017
By visualizing how three neural proteins interact with one another, researchers have revealed how they help groups of brain cells release chemical messages at the same time.
The work describes a surprising new cooperation among the three proteins, and could offer insight into other processes where cells secrete molecules, including insulin and airway mucus. Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) Investigator Axel Brunger and colleagues report the results August 24 in the journal Nature.
When a group of neurons receives an electrical signal, the cells release chemicals called neurotransmitters nearly instantaneously – within less than one thousandth of a second. Neurons hold neurotransmitters in bubble-like structures called synaptic vesicles.
These structures rest inside the end of long, thin projections that point toward neighboring cells. To free neurotransmitters from their bubbles, neurons must fuse vesicle membranes with the outer membrane of the projections. This opens the bubbles and dumps their contents into the space between cells. The chemical signals then float to neighboring cells to relay a message.
Scientists knew that three proteins are involved in spitting out neurons' chemical signals. A group of proteins called SNAREs provides energy for membrane fusion. Another protein, called synaptotagmin, releases neurotransmitters when calcium ions appear following an electrical signal. A third protein, complexin, prevents cells from spontaneously releasing neurotransmitters. Synaptotagmin and complexin each partner with SNARE proteins, but until now, scientists could not explain how these three components worked together.
Brunger's team at Stanford University synthesized portions of each component, allowed them to assemble into a complex, and coaxed the complex to form crystals. Then they determined the structure of the complex by measuring how the crystals diffracted x-ray light.
The crystal structure revealed two ways that the proteins interact. The first interaction – between synaptotagmin and the SNARE proteins – is identical to one Brunger and colleagues described in a 2015 paper in Nature. A second, unexpected, interaction revealed a relationship between all three components in the larger complex.
In this three-component interaction, a curly helix of complexin nestles near a helix in a synaptotagmin protein, arranged so that twists of the helices align like the threads of a screw. These helices also rest atop helices of the SNARE complex.
In collaboration with HHMI Investigator Thomas Südhof, the researchers engineered mouse neurons to produce mutated synaptotagmin proteins, which weakened the attraction between the three proteins. Cells with mutated proteins, or ones that lacked complexin, lost the ability to synchronize neurotransmitter release.
Based on their observations, the researchers propose that the three-part interaction locks down the SNARE proteins, so they cannot perform the membrane fusion required for neurotransmitter release until the right moment. Complexin pins the three proteins together, and synaptotagmin might unlock the SNARE proteins when triggered by calcium ions.
“This tripartite interaction intuitively explains the role of the three components,” Brunger says. “Now we can explain the cooperation between complexin, synaptotagmin, and the SNARE complex.”
There are more than 60 different SNARE proteins in mammalian cells, which, along with various forms of synaptotagmin, are involved in hormone release and other cellular processes. A similar three-part interaction involving SNARE proteins may be used for other calcium-dependent cellular release processes too, Brunger says.
###
Qiangjun Zhou et al. “The primed SNARE-complexin-synaptotagmin complex for neuronal exocytosis,” Nature 548 (August 24, 2017): 420-425, doi: 10.1038/nature23484.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Sea slugs inspire highly stretchable biomedical sensor
USC Viterbi School of Engineering researcher Hangbo Zhao presents findings on highly stretchable and customizable microneedles for application in fields including neuroscience, tissue engineering, and wearable bioelectronics. The revolution in…

Twisting and binding matter waves with photons in a cavity
Precisely measuring the energy states of individual atoms has been a historical challenge for physicists due to atomic recoil. When an atom interacts with a photon, the atom “recoils” in…

Nanotubes, nanoparticles, and antibodies detect tiny amounts of fentanyl
New sensor is six orders of magnitude more sensitive than the next best thing. A research team at Pitt led by Alexander Star, a chemistry professor in the Kenneth P. Dietrich…





















