Artificial intelligence for complex materials
Machine learning solver for materials' mechanics
J. R. Mianroodi, Max-Planck-Institut für Eisenforschung GmbH
Max Planck researchers present a new deep neural network for predicting materials’ mechanical behaviour.
Predicting the mechanical behaviour of all the systems that surround us, from vehicles and spaceships to bridges and skyscrapers, is essential for safety and design. Since more than 300 years, scientists know how to cast the underlying physics into a mathematical formulation, and thanks to technological progress a huge collection of numerical tools and methods have been developed to computationally solve the complex equations and predict correct answers in various mechanical problems.
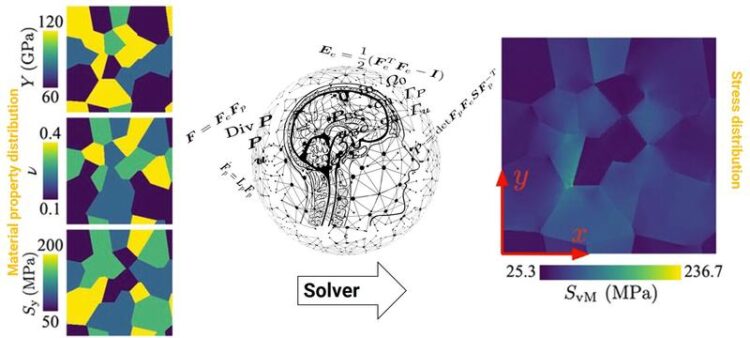
However, solving these equations directly consumes time and gets more difficult, the more complex the system is, forcing researchers to use approximations rather than all variables of the system. Now, a huge step towards accurate and fast predictions of complex materials’ mechanics was made. Scientists from the Max-Planck-Institut für Eisenforschung (MPIE) and DeepMetis, a venture specialized on artificial intelligence in Berlin, used deep neural networks to calculate local stress in complex materials and this, up to 8300 times faster than a standard solver would do. They published their latest findings in the journal npj Computational Materials.
“Our latest work shows how all these calculations can be replaced by machine learning. Instead of solving the equations directly, we developed a neural network that can learn the physics and predict correct answers to complex and nonlinear mechanics questions simply by looking at a large set of data.”, explains Dr. Jaber Rezaei Mianroodi, head of the MPIE group “Computational Sustainable Metallurgy” and first author of the publication. After being trained with precomputed correct physical responses, the neural network is able to predict solutions to problems and configurations it never encountered during the training. Much like an experienced engineer who develops an intuition for complex mechanical problems and is able to make educated guesses in seconds, the network appears to learn the underlying physics and predict solutions in microseconds. The network’s predictions are orders of magnitude faster than conventional solvers despite of the nonlinearity or complexity of the system. Unlike conventional solvers, which require an iterative (trial and error) approach to solving nonlinear problems, the trained machine learning solver is not iterative.
“This method can replace the conventional solvers and enhances our understanding of multiscale and multiphysics problems. Our solver consumes orders of magnitude less computation time, opening up new possibilities for advanced material models. Incorporating our machine learning technique will help us make the models more predictive and realistic as it allows to optimize even more complicated systems.”, says Dr. Nima Siboni, expert for artificial intelligence at DeepMetis and alumni of the MPIE. The researchers will now extend the flexibility and scope of the machine learning approach to make even more accurate predictions. They also plan to investigate other important equations that are time-consuming to solve using conventional methods.
Wissenschaftliche Ansprechpartner:
Dr. Jaber Rezaei Mianroodi, j.mianroodi@mpie.de
Originalpublikation:
J. R. Mianroodi, N. H. Siboni, D. Raabe: Teaching solid mechanics to artificial intelligence – a fast solver for heterogeneous materials. In: npj Compu Mats, 10.1038/s41524-021-00571-z
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Information Technology
Here you can find a summary of innovations in the fields of information and data processing and up-to-date developments on IT equipment and hardware.
This area covers topics such as IT services, IT architectures, IT management and telecommunications.
Newest articles

Microscopic basis of a new form of quantum magnetism
Not all magnets are the same. When we think of magnetism, we often think of magnets that stick to a refrigerator’s door. For these types of magnets, the electronic interactions…

An epigenome editing toolkit to dissect the mechanisms of gene regulation
A study from the Hackett group at EMBL Rome led to the development of a powerful epigenetic editing technology, which unlocks the ability to precisely program chromatin modifications. Understanding how…

NASA selects UF mission to better track the Earth’s water and ice
NASA has selected a team of University of Florida aerospace engineers to pursue a groundbreaking $12 million mission aimed at improving the way we track changes in Earth’s structures, such…