The highs and lows of Martian Water Vapour
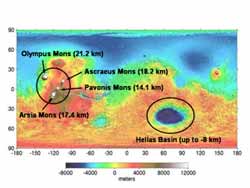
Measurements of water vapour in the atmosphere of Mars by the PFS (Planetary Fourier Spectrometer) and OMEGA (Observatoire pour la Minéralogie, l’Eau, les Glaces, et l’Activité) instruments, both onboard Mars Express, give us a clear view on the seasonal behaviour of water vapour in the atmosphere of Mars. The study shows irregularities in the behaviour of water vapour, different from the global trend on Mars, in the atmosphere surrounding the Big Volcanoes and the Hellas Basin, which are respectively the highest and lowest regions on Mars.
There have been regular measurements of the behaviour of water vapour during the Martian year since the 1970s, but the complementary characteristics of these two instruments allow a comprehensive analysis of the Martian water cycle with unprecedented detail.
“For most of the year, the atmosphere on the summit of the big volcanoes is enriched in water vapour – the ratio of water vapour is much higher compared to the surrounding areas. This can be explained by upslope currents activated by the extreme topography of the region that bring up a lot of material, water vapour included, from the bottom to the summit,” said Luca Maltagliati, a scientist at the Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research.
In the Hellas Basin region, the observations also showed a peculiar seasonal behaviour. While the north seems to present the same quantity of water vapour through the Martian year, the interior of the basin seems to be depleted of it in some seasons, especially if compared to the south region.
The causes for this are still being investigated but it is believed that, in this case, local circulation of the atmosphere plays an important role. In fact, Hellas itself is known to have an important part in driving the circulation of the whole Southern hemisphere of Mars. The presence of surface ice was also observed during local winter.
These results mark the importance of local influence on the global water cycle.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

A universal framework for spatial biology
SpatialData is a freely accessible tool to unify and integrate data from different omics technologies accounting for spatial information, which can provide holistic insights into health and disease. Biological processes…

How complex biological processes arise
A $20 million grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) will support the establishment and operation of the National Synthesis Center for Emergence in the Molecular and Cellular Sciences (NCEMS) at…

Airborne single-photon lidar system achieves high-resolution 3D imaging
Compact, low-power system opens doors for photon-efficient drone and satellite-based environmental monitoring and mapping. Researchers have developed a compact and lightweight single-photon airborne lidar system that can acquire high-resolution 3D…





















