Emergence of "Devil's staircase"
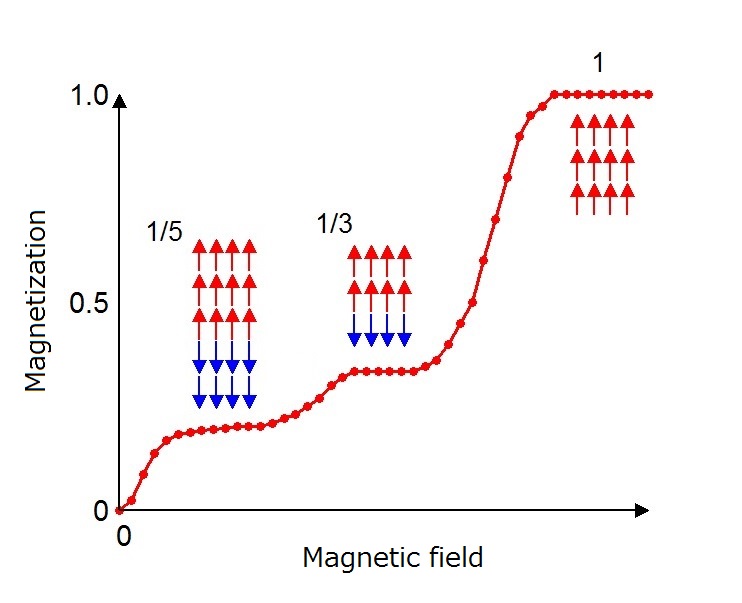
The magnetic structure that gives rise to the Devil's Staircase. Magnetization (vertical axis) of cobalt oxide shows plateau like behaviors as a function of the externally-applied magnetic field (horizontal axis). The researchers succeeded in determining the magnetic structures which create such plateaus. Red and blue arrows indicate spin direction. Copyright : © 2015 Hiroki Wadati.
Researchers at the University of Tokyo have revealed a novel magnetic structure named the “Devil’s staircase” in cobalt oxides using soft X-rays.
This is an important result since the researchers succeeded in determining the detailed magnetic structure of a very small single crystal invisible to the human eye.
Recent remarkable progress in resonant soft x-ray diffraction performed in synchrotron facilities has made it possible to determine spin ordering (magnetic structure) in small-volume samples including thin films and nanostructures, and thus is expected to lead not only to advances in materials science but also application to spintronics, a technology which is expected to form the basis of future electronic devices.
Cobalt oxide is known as one material that is suitable for spintronics applications, but its magnetic structure was not fully understood.
The research group of Associate Professor Hiroki Wada at the University of Tokyo Institute for Solid State Physics, together with the researchers at Kyoto University and in Germany, performed a resonant soft X-ray diffraction study of cobalt (Co) oxides in the synchrotron facility BESSY II in Germany.
They observed all the spin orderings which are theoretically possible and determined how these orderings change with the application of magnetic fields.
The plateau-like behavior of magnetic structure as a function of magnetic field is called the “Devil’s staircase,” and is the first such discovery in spin systems in 3D transition metal oxides including cobalt, iron, manganese.
By further resonant soft X-ray diffraction studies, one can expect to find similar “Devil’s staircase” behavior in other materials. By increasing the spatial resolution of microscopic observation of the “Devil’s staircase” may lead to the development of novel types of spintronics materials.
Associated links
UTokyo Research article
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

A universal framework for spatial biology
SpatialData is a freely accessible tool to unify and integrate data from different omics technologies accounting for spatial information, which can provide holistic insights into health and disease. Biological processes…

How complex biological processes arise
A $20 million grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) will support the establishment and operation of the National Synthesis Center for Emergence in the Molecular and Cellular Sciences (NCEMS) at…

Airborne single-photon lidar system achieves high-resolution 3D imaging
Compact, low-power system opens doors for photon-efficient drone and satellite-based environmental monitoring and mapping. Researchers have developed a compact and lightweight single-photon airborne lidar system that can acquire high-resolution 3D…





















