New remote-controlled 'smart' platform helps in cardiovascular disease treatment
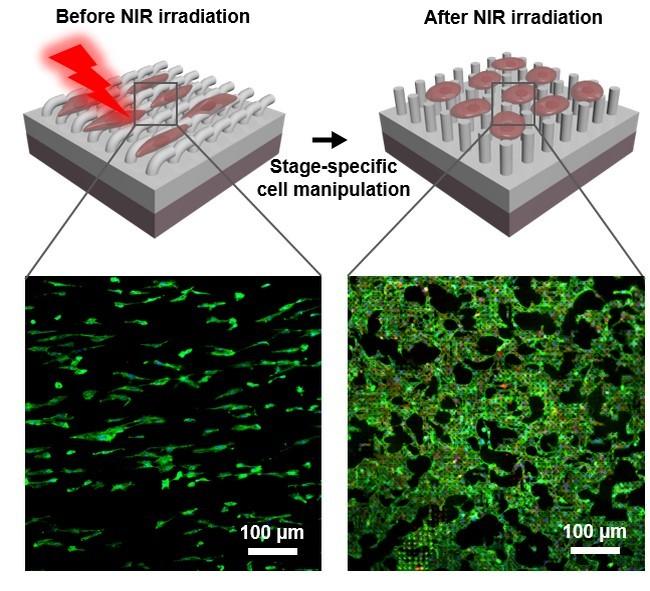
A schematic illustration of the step-wise modulation of different behaviors of vascular endothelial cells by a NIR-controlled topographically dynamic platform Credit: DU Xuemin
Rapid endothelialization poses challenges, however, when using existing synthetic biomaterials, due to their static properties. Such materials cannot offer dynamic, on-demand means for manipulating specific vascular endothelial cell functions at different stages of endothelium remodeling.
A joint research group led by Dr. DU Xuemin at the Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences recently demonstrated a remote-controlled “smart” platform that effectively directs programmed vascular endothelium remodeling in a temporally controllable manner. The study was published in National Science Review [2019].
The researchers first prepared a bilayer platform with programmable surface topographies using a shape-memory polymer and gold nanorods acting as a photothermal agent. The bilayer platform allowed on-demand manipulation of vascular endothelial cell functions, thus meeting the requirements of endothelium remodeling.
During the endothelialization process of native blood vessels, vascular endothelial cells and progenitor cells are first recruited to regeneration sites. This is followed by the adhesion and spreading of the vascular endothelial cells to form a confluent vascular endothelial cell monolayer. In the human body, such a process is implemented through extracellular matrix (ECM)-mediated stepwise modulation of vascular endothelial cell functions at different stages.
“The new platform possesses originally stable anisotropic microgroove array topography. This topography can significantly direct cell polarization and thereby enhance the collective migration of vascular endothelial cells,” said ZHAO Qilong, first author of the study.
Upon 10 s of near-infrared (NIR) irradiation, the heat generated on the bottom layer induced the surface topographies of the platform to change from their original anisotropic microgroove array to a permanent isotropic micropillar array.
The focal adhesion and spreading of vascular endothelial cells were subsequently promoted at the later stage of endothelialization by the platform after the topographies were changed. The remote-controlled “smart” platform promoted different functions of vascular endothelial cells in turn, thus mimicking dynamic ECM-mediated effects throughout the endothelialization process for the first time using synthetic biomaterials.
“Traditionally, biomaterials and tissue engineering scaffolds offer suitable platforms to support cell attachment and ingrowth. We aim to develop biomaterials with dynamic properties to actively modulate different cell functions in specific spatiotemporal manners, just like the native ECM in our bodies. We believe biomaterials with dynamic properties will contribute to the progress of wound healing and complex tissue/organ regeneration,” said Dr. DU Xuemin from SIAT.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/nsr/nwz188All latest news from the category: Health and Medicine
This subject area encompasses research and studies in the field of human medicine.
Among the wide-ranging list of topics covered here are anesthesiology, anatomy, surgery, human genetics, hygiene and environmental medicine, internal medicine, neurology, pharmacology, physiology, urology and dental medicine.
Newest articles

A universal framework for spatial biology
SpatialData is a freely accessible tool to unify and integrate data from different omics technologies accounting for spatial information, which can provide holistic insights into health and disease. Biological processes…

How complex biological processes arise
A $20 million grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) will support the establishment and operation of the National Synthesis Center for Emergence in the Molecular and Cellular Sciences (NCEMS) at…

Airborne single-photon lidar system achieves high-resolution 3D imaging
Compact, low-power system opens doors for photon-efficient drone and satellite-based environmental monitoring and mapping. Researchers have developed a compact and lightweight single-photon airborne lidar system that can acquire high-resolution 3D…





















