NASA Satellite sees most of Cyclone Bingiza's rainfall over Mozambique Channel
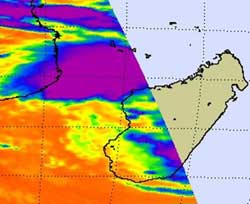
NASA\'s Aqua satellite captured cold thunderstorm cloud tops (purple) to the north and west of the center of Tropical Storm Bingiza in this infrared image of Feb. 15 at 11:11 UTC. Credit: NASA JPL, Ed Olsen<br>
When NASA's Aqua satellite flew over Madagascar this morning, Feb. 15 at 11:11 UTC (6:11 a.m. EST), the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument read the temperatures of the cold thunderstorm cloud tops in Cyclone Bingiza. Most of the strongest thunderstorms were north and west of the center of circulation already over the Mozambique Channel, while Bingiza's center remains over the western part of the island nation.
At 0900 UTC (4 a.m. EST) on Feb. 15, Tropical Cyclone Bingiza had maximum sustained winds near 35 knots (40 mph/64 kmh) so it was still a tropical storm. It was centered about 180 miles (289 km) north-northwest of Antananarivo, Madagascar, near 16.4 South and 45.2 East. It was moving west near 10 knots (11 mph/18 kmh).
At 1 a.m. EST (0600 UTC) Majunga, Madagascar reported north winds at 17 knots (20 mph/31 kmh) and an atmospheric pressure of 997 millibars. Majunga is a seaport city, a district, and a province on the northwest coast of Madagascar. Mahajanga is the capital city of the Boeny region as well as the Mahajanga Province.
Forecasters at the Joint Typhoon Warning Center expect Bingiza to move entirely into the eastern Mozambique Channel later today. A trough (elongated area) of low pressure will then push Bingiza parallel to the western coastline of Madagascar and forecasters expect the warm waters of the Channel and the low wind shear to allow it to re-strengthen. Bingiza is expected to turn toward the east and make a second landfall in southwestern Madagascar later this week.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.nasa.govAll latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

A universal framework for spatial biology
SpatialData is a freely accessible tool to unify and integrate data from different omics technologies accounting for spatial information, which can provide holistic insights into health and disease. Biological processes…

How complex biological processes arise
A $20 million grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) will support the establishment and operation of the National Synthesis Center for Emergence in the Molecular and Cellular Sciences (NCEMS) at…

Airborne single-photon lidar system achieves high-resolution 3D imaging
Compact, low-power system opens doors for photon-efficient drone and satellite-based environmental monitoring and mapping. Researchers have developed a compact and lightweight single-photon airborne lidar system that can acquire high-resolution 3D…





















