NASA and NOAA satellite data see North Atlantic system more concentrated
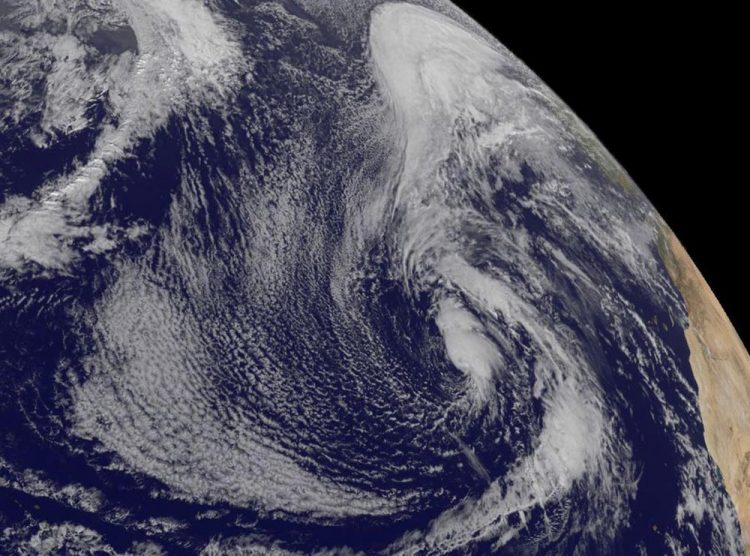
This visible image of the low pressure area in the Central North Atlantic Ocean was taken from NOAA's GOES-East satellite on Jan. 12 at 1445 UTC (9:45 a.m.) EST. Africa is seen to the right. Credit: NASA/NOAA GOES Project
NOAA's National Hurricane Center (NHC) noted the development of the extra-tropical low pressure area on Sunday, January 10 at 1:50 p.m. EST.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder known as the AIRS instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite measured temperatures in the system's cloud tops on Jan. 11 at 0435 (Jan. 10 at 11:35 p.m. EST) and later at 1541 UTC (10:41 a.m. EST). AIRS provides valuable temperature data such as cloud top and sea surface temperatures. AIRS saw the coldest cloud top temperatures near -63F/-53C and strongest storms expanded from east of center to around the center of this out-of-season extra-tropical low pressure area.
NOAA's GOES-East satellite captured a visible image of the low pressure area on Jan. 12 at 1445 UTC (9:45 a.m.) EST. Clouds and storms surrounded the center of circulation and in a band east of the center. The low pressure area has been designated “System 90L.”
On Jan. 12 at 2 p.m. EST, the low was centered 1,100 miles southwest of the Azores, an archipelago in the mid-Atlantic. The National Hurricane Center noted that cloudiness and thunderstorms have become a little more concentrated and organized near the center of the storm's circulation. The low was producing winds to near 60 mph over the southern and eastern quadrants of its circulation. The cyclone is expected to move eastward to northeastward over the eastern subtropical Atlantic over the next couple of days.
NHC said “Although environmental conditions are only marginally conducive for development, this system could become a subtropical or tropical storm within the next day or so. Regardless of subtropical or tropical cyclone formation, this system is expected to produce hazardous marine conditions over portions of the eastern Atlantic for the next few days.”
The National Hurricane Center gives this system a medium chance to develop into a depression over the next five days.
For updated forecasts, visit NHC at http://www.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Why getting in touch with our ‘gerbil brain’ could help machines listen better
Macquarie University researchers have debunked a 75-year-old theory about how humans determine where sounds are coming from, and it could unlock the secret to creating a next generation of more…

Attosecond core-level spectroscopy reveals real-time molecular dynamics
Chemical reactions are complex mechanisms. Many different dynamical processes are involved, affecting both the electrons and the nucleus of the present atoms. Very often the strongly coupled electron and nuclear…

Free-forming organelles help plants adapt to climate change
Scientists uncover how plants “see” shades of light, temperature. Plants’ ability to sense light and temperature, and their ability to adapt to climate change, hinges on free-forming structures in their…





















