NASA's TRMM satellite sees some heavy rainfall in Typhoon Sanvu
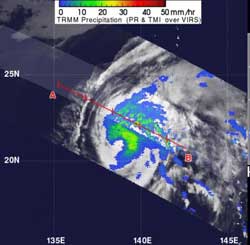
This TRMM image of rainfall from Typhoon Sanvu was taken on May 24, 2012. Sanvu's heaviest rainfall was occurring in its northeastern quadrant where some intense storms were dropping rainfall at a rate greater than 50mm/hr (~2 inches/hr). TRMM shows that the rainfall wraps around the eastern side of the storm, stretching from north to south, while the western side of the storm is deficient in rainfall. Light to moderate rainfall was falling at a rate between .78 inches and 1.57 inches per hour (20 to 40 mm).<br><br>Credit: NASA/TRMM, Hal Pierce<br>
The TRMM satellite measured the rainfall from Typhoon Sanvu on May 24, 2012.TRMM's Microwave Imager (TMI) and Precipitation Radar (PR) data shows that Sanvu's heaviest rainfall was occurring in its northeastern quadrant where some intense storms were dropping rainfall at a rate greater than 50mm/hr (~2 inches/hr).
TRMM shows that the rainfall wraps around the eastern side of the storm, stretching from north to south, while the western side of the storm is deficient in rainfall.
On May 24 at 1500 UTC (11 a.m. EDT/U.S.), Typhoon Sanvu had maximum sustained winds near 65 knots (75 mph/120.4 kph). It was about 275 nautical miles south-southwest of Iwo To, Japan, near 21.2 North and 138.9 East.
Sanvu is causing high waves throughout the region, and waves have been estimated as high as 29 feet (8.8 meters). It is moving to the north at 9 knots (10.3 mph/16.6 kph).
Forecasters at the Joint Typhoon Warning Center now forecast the Sanvu will likely take a track very close to the island of Iwo To, Japan early on May 26. Iwo To was reporting thunderstorms and winds from the east-southeast by mid-day (U.S. EDT) on May 24 (May 25 local time) which are associated with the east-southeasterly flow from the approaching typhoon.
As Sanvu continues to approach, thunderstorms from the typhoon will be affecting the island on May 26.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.nasa.govAll latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

A universal framework for spatial biology
SpatialData is a freely accessible tool to unify and integrate data from different omics technologies accounting for spatial information, which can provide holistic insights into health and disease. Biological processes…

How complex biological processes arise
A $20 million grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) will support the establishment and operation of the National Synthesis Center for Emergence in the Molecular and Cellular Sciences (NCEMS) at…

Airborne single-photon lidar system achieves high-resolution 3D imaging
Compact, low-power system opens doors for photon-efficient drone and satellite-based environmental monitoring and mapping. Researchers have developed a compact and lightweight single-photon airborne lidar system that can acquire high-resolution 3D…





















