Black nitrogen: Bayreuth researchers discover new high-pressure material and solve a puzzle of the periodic table
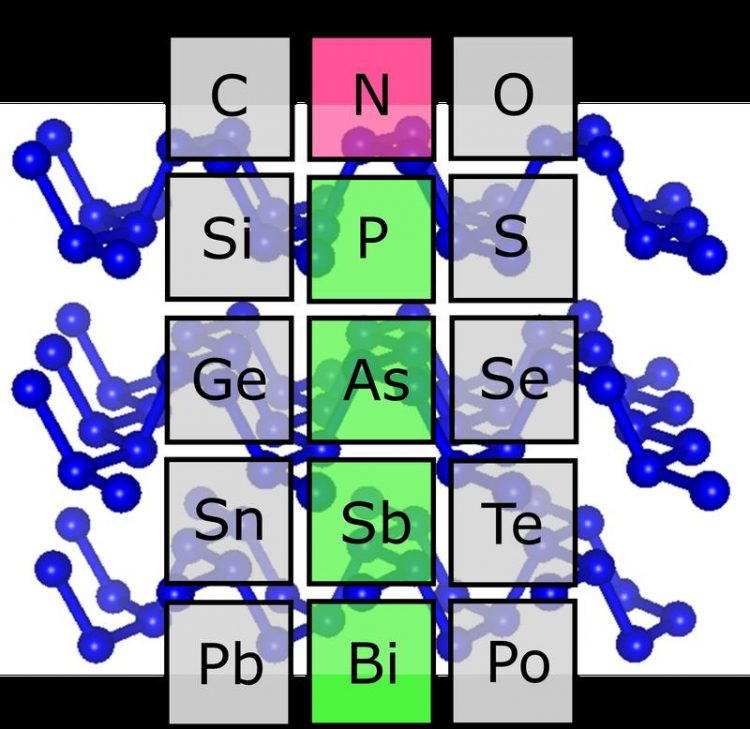
Under extremely high pressures, nitrogen (red), like the heavier elements phosphorus, arsenic, antimony and bismuth (green), has a structure consisting of zigzag-shaped two-dimensional layers. Image: Dominique Laniel
Nitrogen – an exception in the periodic system?
When you arrange the chemical elements in ascending order according to their number of protons, and look at their properties, it soon becomes obvious that certain properties recur at large intervals (“periods”).
The periodic table of elements brings these repetitions into focus. Elements with similar properties are placed one below the other in the same column, and thus form a group of elements. At the top of a column is the element that has the fewest protons and the lowest weight compared to the other group members.
Nitrogen heads element group 15, but was previously considered the “black sheep” of the group. The reason: in earlier high-pressure experiments, nitrogen showed no structures similar to those the heavier elements of this group – especially phosphorus, arsenic, and antimony – exhibit under normal conditions.
Instead, exactly this kind of similarities could be observed at high pressures in the neighbouring groups headed by carbon and oxygen.
Black nitrogen – a high-pressure material with technologically attractive properties
In fact, nitrogen is no exception after all. Researchers at the Bavarian Research Institute of Experimental Geochemistry & Geophysics (BGI) and the Laboratory for Crystallography at the University of Bayreuth have now been able to prove this with the help of a measuring method they recently developed.
Under the leadership of Dr. Dominique Laniel, they have made an unusual discovery. At very high pressures and temperatures, nitrogen atoms form a crystalline structure that is characteristic of black phosphorus, which is a particular variant of phosphorus.
It also occurs in arsenic and antimony. This structure is composed of two-dimensional layers in which nitrogen atoms are cross-linked in a uniform zigzag pattern. In terms of their conductive properties, these 2D layers are similar to graphene, which shows great promise as a material for high-tech applications. Therefore, black phosphorus is currently being studied for its potential as a material for highly efficient transistors, semiconductors, and other electronic components in the future.
The Bayreuth researchers are proposing an analogous name for the allotrope of nitrogen they have discovered: black nitrogen. Some technologically attractive properties, in particular its directional dependence (anisotropy), are even more pronounced than in black phosphorus.
However, black nitrogen can only exist thanks to the exceptional pressure and temperature conditions under which it is produced in the laboratory. Under normal conditions it dissolves immediately.
“Because of this instability, industrial applications are currently not feasible. Nevertheless, nitrogen remains a highly interesting element in materials research. Our study shows by way of example that high pressures and temperatures can produce material structures and properties that researchers previously did not know existed,” says Laniel.
Determining structure with particle accelerators
It took truly extreme conditions to produce black nitrogen. The compression pressure was 1.4 million times the pressure of the Earth's atmosphere, and the temperature exceeded 4,000 degrees Celsius. To find out how atoms arrange themselves under these conditions, the Bayreuth scientists cooperated with the German Electron Synchrotron (DESY) in Hamburg and the Advanced Photon Source (APS) at the Argonne National Laboratory in the USA.
Here, X-rays generated by particle acceleration were fired at the compressed samples. “We were surprised and intrigued by the measurement data suddenly providing us with a structure characteristic of black phosphorus. Further experiments and calculations have since confirmed this finding.
This means there is no doubt about it: nitrogen is, in fact, not an exceptional element, but follows the same golden rule of the periodic table as carbon and oxygen do,” says Laniel, who came to the University of Bayreuth in 2019 as an Alexander von Humboldt Foundation research fellow.
International cooperation
In addition to the German Electron Synchrotron (DESY) in Hamburg and the Advanced Photon Source (APS) in Illinois/USA, both Goethe University Frankfurt, and the international software company BIOVIA participated in the new study as research partners of the University of Bayreuth.
Research funding
The research work at the University of Bayreuth was funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG), the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF), and the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation.
Dr. Dominique Laniel
Laboratory of Crystallography
University of Bayreuth
Dominique.Laniel@uni-bayreuth.de
Prof. Dr. Leonid Dubrovinsky
Bavarian Research Institute of Experimental Geochemistry & Geophysics (BGI)
University of Bayreuth
Phone: +49 (0)92155 -3736 oder -3707
Leonid.Dubrovinsky@uni-bayreuth.de
Prof. Dr. Natalia Dubrovinskaia
Laboratory of Crystallography
University of Bayreuth
Phone: +49 (0)92155 -3880 oder -3881
Natalia.Dubrovinskaia@uni-bayreuth.de
Dominique Laniel et al.: High-pressure polymeric nitrogen allotrope with the black phosphorus structure. Physical Review Letters (2020), DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.124.216001
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

Trotting robots reveal emergence of animal gait transitions
A four-legged robot trained with machine learning by EPFL researchers has learned to avoid falls by spontaneously switching between walking, trotting, and pronking – a milestone for roboticists as well…

Innovation promises to prevent power pole-top fires
Engineers in Australia have found a new way to make power-pole insulators resistant to fire and electrical sparking, promising to prevent dangerous pole-top fires and reduce blackouts. Pole-top fires pose…

Possible alternative to antibiotics produced by bacteria
Antibacterial substance from staphylococci discovered with new mechanism of action against natural competitors. Many bacteria produce substances to gain an advantage over competitors in their highly competitive natural environment. Researchers…





















