A pulse of innovation: AI at the service of heart research
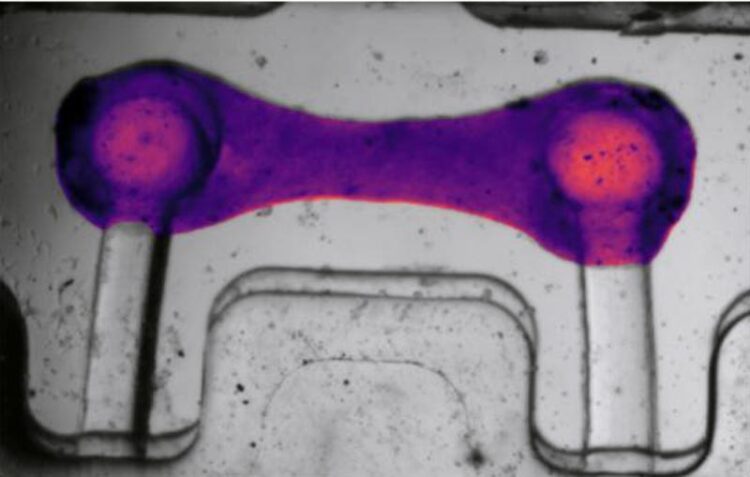
As seen through computer vision, BeatProfiler in action applied to cardiac tissue
Credit: Youngbin Kim/Columbia Engineering
Columbia biomedical engineers use AI to build a transformative new tool to study and diagnose heart function.
Understanding heart function and disease, as well as testing new drugs for heart conditions, has long been a complex and time-consuming task. A promising way to study disease and test new drugs is to use cellular and engineered tissue models in a dish, but existing methods to study heart cell contraction and calcium handling require a good deal of manual work, are prone to errors, and need expensive specialized equipment. There clearly is a critical medical need for a more efficient, accurate, and accessible way to study heart function, using a methodology based on artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning.
BeatProfiler, new tool to rapidly analyze heart cell function
Researchers at Columbia Engineering unveiled a groundbreaking new tool today that addresses these challenges head-on. BeatProfiler is a comprehensive software that automates the analysis of heart cell function from video data and is the first system to integrate the analysis of different heart function indicators, such as contractility, calcium handling, and force output into one tool, speeding up the process significantly and reducing the chance for errors. BeatProfiler enabled the researchers to not only distinguish between different diseases and levels of their severity but also to rapidly and objectively test drugs that affect heart function. The study was published on April 8 in IEEE Open Journal of Engineering in Medicine and Biology.
“This is truly a transformative tool,” said project leader Gordana Vunjak-Novakovic, University Professor and the Mikati Foundation Professor of Biomedical Engineering, Medical Sciences, and Dental Medicine at Columbia. “It’s fast, comprehensive, automated, and compatible with a broad range of computer platforms so it is easily accessible to investigators and clinicians.”
Software is open-source
The team, which included Barry Fine, assistant professor of medicine (in Cardiology) at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, elected not to file a patent application, and instead are offering the AI software as open source, so it can be directly used — for free — by any lab. They believe that this is important for disseminating the results of their research, as well as for getting feedback from users in academic, clinical, and commercial labs that can help the team to further refine the software.
The need to diagnose heart disease quickly and accurately
This project was driven, like much of Vunjak-Novakovic’s research, by a clinical need to diagnose heart diseases more quickly and accurately. This was a project that was several years in the making in which the team added different features piece by piece. While the overarching need was to develop a tool that could better capture the function of the cardiac models that the team was building to study cardiac diseases and assess the efficacy of potential therapeutics, the researchers had an urgent need to quickly and accurately assess the function of their cardiac models in real-time.
As the lab was making more and more cardiac tissues through innovations such as milliPillar and multiorgan tissue models, the increased capabilities of the tissues required the researchers to develop a method to more rapidly quantify the function of cardiomyocytes (heart muscle cells) and tissues to enable studies exploring genetic cardiomyopathies, cosmic radiation, immune-mediated inflammation, and drug discovery.
Collaborators in software development, machine learning, and more
In the last year and a half, lead author Youngbin Kim and his coauthors developed a graphical user interface (GUI) on top of the code so that biomedical researchers with no coding expertise could easily analyze the data with just a few clicks. This brought together experts in software development (for the GUI development), machine learning (for developing computer vision technology and disease/drug classifiers), signal processing (for processing contractile and calcium signals), engineering (translating pillar deflection on the cardiac platform to mechanical force), and user experience by lab members (to give feedback for improvements in the interface).
The results
The study showed that BeatProfiler could accurately analyze cardiomyocyte function, outperforming existing tools by being faster — up to 50 times in some cases — and more reliable. It detected subtle changes in engineered heat tissue force response that other tools might miss.
“This level of analysis speed and versatility is unprecedented in cardiac research,” said Kim, a PhD candidate in Vunjak-Novakovic’s lab at Columbia Engineering. “Using machine learning, the functional measurements analyzed by BeatProfiler helped us to distinguish between diseased and healthy heart cells with high accuracy and even to classify different cardiac drugs based on how they affect the heart.”
What’s next
The team is working to expand BeatProfiler’s capabilities for new applications in heart research, including a full spectrum of diseases that affect the pumping of the heart, and drug development. To ensure that BeatProfiler can be applied to a wide variety of research questions, they are testing and validating its performance across additional in vitro cardiac models, including different engineered heart tissue models. They are also refining their machine-learning algorithm to extend and generalize its use to a variety of heart diseases and drug effect classification. The long-term goal is to adapt BeatProfiler to pharmaceutical settings to speed up the testing of hundreds of thousands of candidate drugs at once.
###
About the Study
Journal: IEEE Open Journal of Engineering in Medicine and Biology
The study is titled “BeatProfiler: Multimodal in Vitro Analysis of Cardiac Function Enables Machine Learning Classification of Diseases and Drugs.”
Authors are: Youngbin Kim, Kunlun Wang, Roberta I. Lock, Trevor R. Nash, Sharon Fleischer, Bryan Z. Wang, and Gordana Vunjak-Novakovic, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Columbia Engineering; and Barry M. Fine, Department of Medicine, Division of Cardiology, Columbia University Medical Center.
The work of Gordana Vunjak-Novakovic was supported by the National Institutes of Health under Grants P41 EB027062 and 5R01HL076485-15, in part by the National Science Foundation under Grant NSF1647837, and in part by National Aeronautics and Space Administration under Grant NNX16AO69A. The work of Barry M. Fine was supported in part by the National Institutes of Health under Grant R01HL166387 and in part by Abramova Foundation.
The authors declare no financial or other conflicts of interest.
LINKS:
Paper: https://doi.org/10.1109/OJEMB.2024.3377461
DOI: 10.1109/OJEMB.2024.3377461
Media Contact
Holly Evarts
Columbia University School of Engineering and Applied Science
he2181@columbia.edu
Office: 212-854-3206
Cell: 347-453-7408
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Medical Engineering
The development of medical equipment, products and technical procedures is characterized by high research and development costs in a variety of fields related to the study of human medicine.
innovations-report provides informative and stimulating reports and articles on topics ranging from imaging processes, cell and tissue techniques, optical techniques, implants, orthopedic aids, clinical and medical office equipment, dialysis systems and x-ray/radiation monitoring devices to endoscopy, ultrasound, surgical techniques, and dental materials.
Newest articles

Making diamonds at ambient pressure
Scientists develop novel liquid metal alloy system to synthesize diamond under moderate conditions. Did you know that 99% of synthetic diamonds are currently produced using high-pressure and high-temperature (HPHT) methods?[2]…

Eruption of mega-magnetic star lights up nearby galaxy
Thanks to ESA satellites, an international team including UNIGE researchers has detected a giant eruption coming from a magnetar, an extremely magnetic neutron star. While ESA’s satellite INTEGRAL was observing…

Solving the riddle of the sphingolipids in coronary artery disease
Weill Cornell Medicine investigators have uncovered a way to unleash in blood vessels the protective effects of a type of fat-related molecule known as a sphingolipid, suggesting a promising new…