NASA sees heavy rain continue in Tropical Cyclone Amara
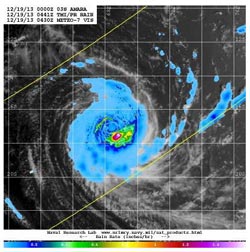
This image of Amara combines TRMM satellite rainfall data and clouds from Japan's METEO-7 satellite on Dec. 19. Heaviest rain was southeast of the center at 1.6 inches per hour.<br><br>Credit: NASA/JAXA/NRL<br>
NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite can measure rainfall rates from space, and that's what it has been doing over Tropical Cyclone Amara since it was born. On Dec. 16, at 2043 UTC/3:43 p.m. EST TRMM data showed scattered bands of moderate to heavy rain falling at a rate of over 76.9 mm/3 inches per hour spiraling into Amara's center. Cloud tops reached 13 km/8 miles high near the center and eastern side.
On Dec. 19 at 0441 UTC, the Naval Research Laboratory in Washington, D.C. combined TRMM satellite rainfall data with a visible image of Amara's clouds from Japan's METEO-7 satellite to provide a complete picture of the storm. The image revealed that the heaviest rain was falling southeast of the center at 1.6 inches/40 mm per hour.
By 0900 UTC/4 a.m. EST, Tropical Cyclone Amara's maximum sustained winds were near 105 knots/120.8 mph/194.5 kph, making it hurricane-strength. Amara was still about 740 nautical miles east-northeast of La Reunion Island, centered near 17.2 south latitude and 68.3 east longitude.
Amara does, however, threaten Rodrigues Island. The Mauritius Meteorological Service or MMS has already put a cyclone class 2 warning in effect for Rodrigues Island. The island is part of the Republic of Mauritius and is located about 350 miles/560 kilometers east of Mauritius.
Amara was moving to the west-southwest at 9 knots and over the next several days is expected to take a more southern route. Occasional showers from Tropical Cyclone Amara are likely on Dec. 20 at night (local time) and will become more frequent, according to the MMS. MMS warns that sustained winds can be expected between 18.6 to 24.8 mph / 30 to 40 kph with gusts to 68.3 mph/75 kph. Amara is also expected to generate rough seas and ocean swells. Maximum significant wave heights can reach 9.1 meters/30 feet.
Amara was moving to the west-southwestward at 9 knots/10.3 mph/16.6 kph. The Joint Typhoon Warning Center expects Amara to continue moving slowly west-southwestward while it remains in a weak steering environment, moving between two deep layer subtropical ridges (elongated areas of high pressure).
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.nasa.govAll latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Webb captures top of iconic horsehead nebula in unprecedented detail
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has captured the sharpest infrared images to date of a zoomed-in portion of one of the most distinctive objects in our skies, the Horsehead Nebula….

Cost-effective, high-capacity, and cyclable lithium-ion battery cathodes
Charge-recharge cycling of lithium-superrich iron oxide, a cost-effective and high-capacity cathode for new-generation lithium-ion batteries, can be greatly improved by doping with readily available mineral elements. The energy capacity and…

Novel genetic plant regeneration approach
…without the application of phytohormones. Researchers develop a novel plant regeneration approach by modulating the expression of genes that control plant cell differentiation. For ages now, plants have been the…





















