NASA's Terra satellite sees Typhoon In-fa stretching
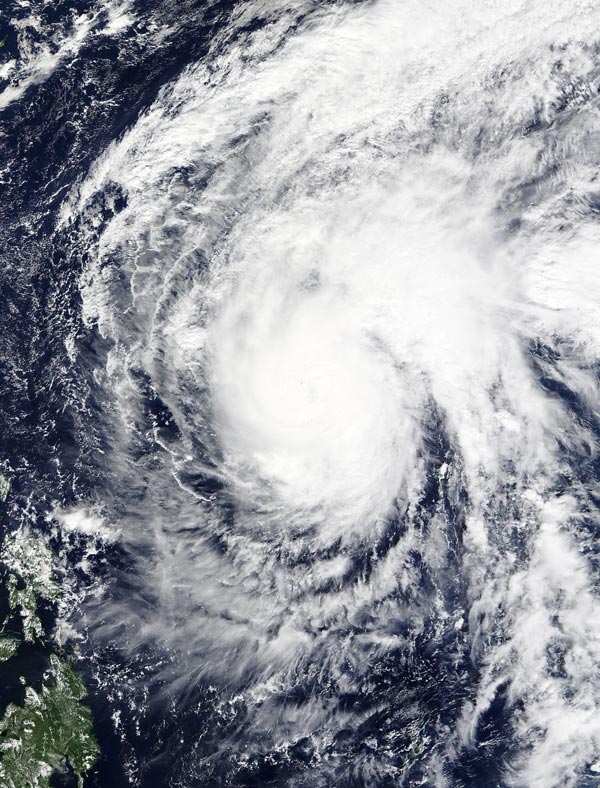
On Nov. 23 at 02:00 UTC the MODIS instrument aboard NASA's Terra satellite captured this image of Typhoon In-fa in the Pacific Ocean. Credits: NASA Goddard MODIS Rapid Response Team
On Nov. 23 at 02:00 UTC (Nov. 22 at 9 p.m. EST) the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument aboard NASA's Terra satellite captured an image of Typhoon In-fa in the Pacific Ocean.
In-fa's cloud-filled eye was surrounded by powerful thunderstorms. A large band of thunderstorms were wrapping into the low-level center in the northeastern quadrant, and stretching east.
Forecasters at the Joint Typhoon Warning Center noted that the system continues to be elongated to the northeast along the leading edge of an approaching mid-Latitude trough (elongated area of low pressure).
On Nov. 23 at 1500 UTC (10 a.m. EST), Typhoon In-fa had maximum sustained winds near 90 knots (103.6 mph/ 166.7 kph). Typhoon-force winds only extend nautical 25 miles (28.7 miles/46.3 km) from the center.
It was centered near 16.9 north latitude and 131.3 east longitude, about 734 nautical miles (844.7 miles/1,359 km) southwest of Iwo To, Japan.
In-fa was moving to the north-northwest at 4 knots (4.6 mph/7.4 kph) and is expected to curve to the northeast.
Environmental conditions are expected to continue to deteriorate as vertical wind shear rapidly increases due to the strong westerly winds from the approaching trough.
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center expects In-fa to weaken over the next couple of days and become an extra-tropical storm.
In-fa is forecast to approach the island of Iwo To, Japan on Nov. 26 and move in a northeasterly direction.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Webb captures top of iconic horsehead nebula in unprecedented detail
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has captured the sharpest infrared images to date of a zoomed-in portion of one of the most distinctive objects in our skies, the Horsehead Nebula….

Cost-effective, high-capacity, and cyclable lithium-ion battery cathodes
Charge-recharge cycling of lithium-superrich iron oxide, a cost-effective and high-capacity cathode for new-generation lithium-ion batteries, can be greatly improved by doping with readily available mineral elements. The energy capacity and…

Novel genetic plant regeneration approach
…without the application of phytohormones. Researchers develop a novel plant regeneration approach by modulating the expression of genes that control plant cell differentiation. For ages now, plants have been the…





















