NASA Catches Tropical Cyclone Bakung's Remnants
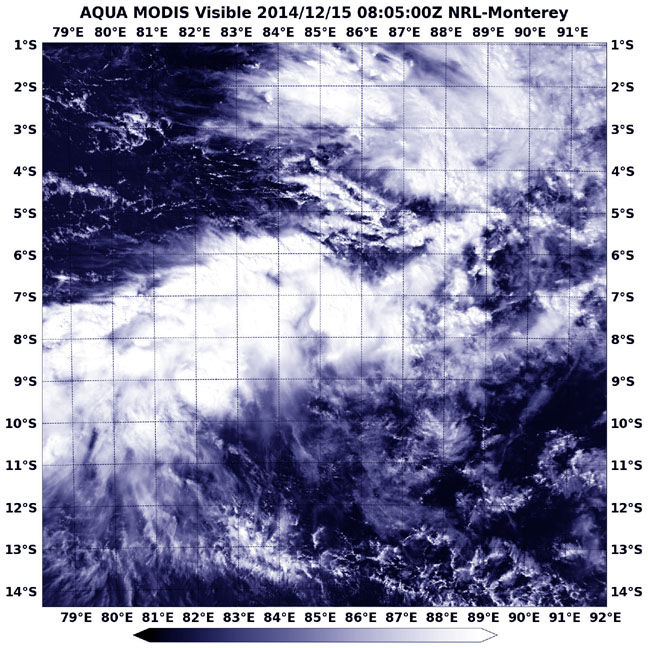
NASA's Aqua satellite captured this image of the remnants of Tropical Cyclone Bakung on Dec. 15 at 08:05 UTC (3:05 a.m. EST). Image Credit: NASA/NRL
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument that flies aboard Aqua captured a visible picture of Bakung's elongated remnants on Dec. 5 at 08:05 UTC (3:05 a.m. EST). The storm appeared to be stretched out from west to east in the visible image.
The last advisory on the tropical cyclone came on Dec. 13 when the storm was still a tropical storm with maximum sustained winds near 35 knots (40 mph/62 kph), but weakening.
Bakung was located near 9.1 south longitude and 89.6 east latitude or about 466 nautical miles (536 miles/863 km) west-northwest of Cocos Islands. It was still moving to the west-northwest at 8 knots (9.2 mph/14.8 kph).
By Dec. 15 the remnants still showed some low-level circulation but it was poorly defined. Bakung's remnant low pressure area was centered near 9.6 south longitude and 85.5 east latitude, 690 nautical miles (794 miles/1,278 km) west of Cocos Island.
Forecasters at the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) noted that an analysis of the upper-level of the troposphere (the layer of atmosphere closest to Earth where weather occurs) showed unfavorable conditions with vertical wind shear blowing as strong as 30 to 40 knots (34 mph/55 kph to 46 mph/74 kph).
The JTWC gives Bakung a low chance of redeveloping in the next day.
Rob Gutro
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/bakung-southern-indian-ocean/All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Recovering phosphorus from sewage sludge ash
Chemical and heat treatment of sewage sludge can recover phosphorus in a process that could help address the problem of diminishing supplies of phosphorus ores. Valuable supplies of phosphorus could…

Efficient, sustainable and cost-effective hybrid energy storage system for modern power grids
EU project HyFlow: Over three years of research, the consortium of the EU project HyFlow has successfully developed a highly efficient, sustainable, and cost-effective hybrid energy storage system (HESS) that…

After 25 years, researchers uncover genetic cause of rare neurological disease
Some families call it a trial of faith. Others just call it a curse. The progressive neurological disease known as spinocerebellar ataxia 4 (SCA4) is a rare condition, but its…





















